Fig. 9. Structural integrative model of the iC3b–CR3 interaction.
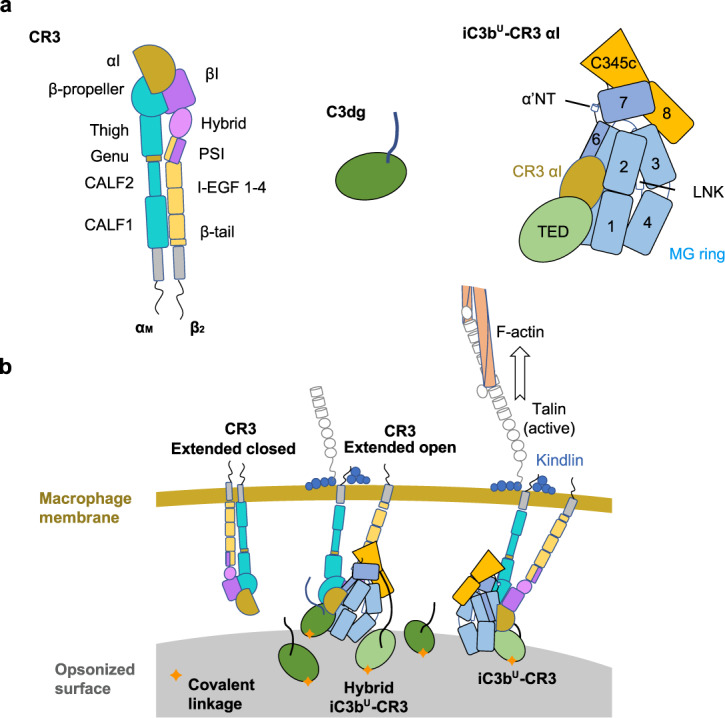
a Schematic representation of CR3 (extended closed conformation), C3dg, and iC3b (upright conformation). Domains and salient features are labeled. b Model of the iC3b–CR3 interaction across the gap between a macrophage (brown band, top) and a heterogeneous iC3b- and C3dg-opsonized surface (grey surface, bottom). iC3b and C3dg are covalently attached to the opsonized surface via a covalent bond involving the Gln991 carbonyl ester (orange star). Two types of iC3b–CR3 (extended open conformation) complexes are depicted: a hybrid complex whereby the TED domain and the C3c subunit in contact with the same CR3 come from different but adjacent iC3b molecules; and a binary heterocomplex involving a single iC3b molecule. The short intracellular region of CR3 is shown interacting with talin and kindlin in some complexes, which in turn recruit the force-producing actomyosin cytoskeleton responsible for the pulling forces necessary for phagocytosis.
