FIGURE 1.
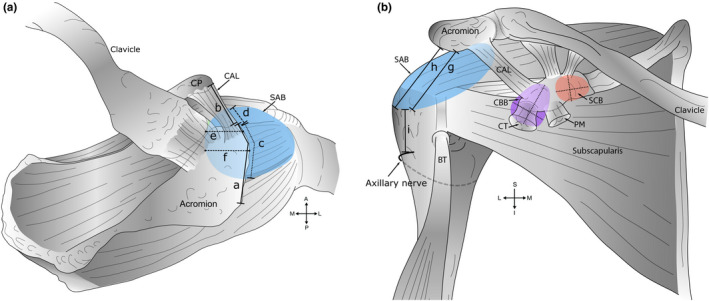
Measurements of bursae and skeletal landmarks. A schematic diagram outlining measurements of bursae obtained during dissection. (a) Superior view. Key: (a) Acromial length. The midpoint of the acromion was defined as half of the acromial length; (b) coracoacromial ligament (CAL) length; (c) anterior‐posterior extent of the subacromial bursa (SAB) along the acromion and (d) coracoacromial ligament; (e) medial extent of the SAB from the anterolateral corner of the acromion; (f) medial extent of the SAB from the midpoint of the acromion, and in relation to the acromioclavicular joint—medial or lateral to the plane of the joint (descriptive only). Measurements ‘e’ and ‘f’ were aligned along the fibres of supraspinatus. (b) Anterior view. Key: Inferior extent of the SAB from the (g) anterolateral corner and (h) midpoint of the acromion; (i) distance from the inferior extent of the SAB to the axillary nerve (anterior branch). Measurements ‘h–i’ were aligned with the shaft of the humerus. Medial‐lateral and superior‐inferior dimension of the coracobrachial (CBB) (shaded purple) and subcoracoid (SCB) bursa (shaded orange), deep to the coracoid process (CP) and conjoint tendon (CT) of coracobrachialis and the short head of biceps brachii. Abbreviations: A, anterior; BT, biceps tendon (long head); I, inferior; L, lateral; M, medial; P, posterior; PM, pectoralis minor; S, superior
