FIGURE 2.
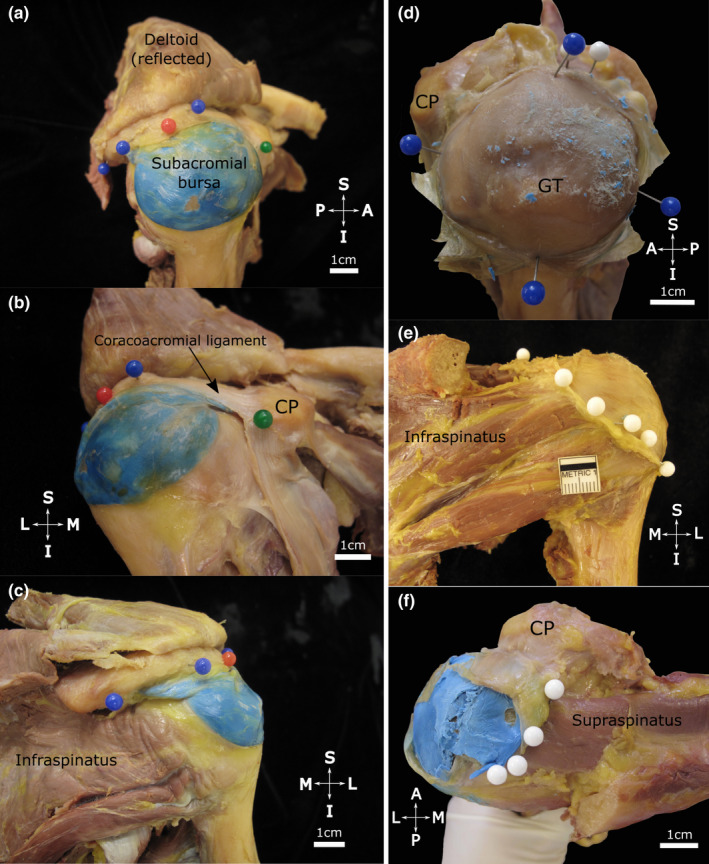
Extent of the subacromial bursa with the coracoacromial arch in situ (a–c) and after resection of the acromion (d–f). The subacromial bursa (injected with blue latex) is situated over the proximal humerus. Note (a, lateral view) its extent along the lateral edge of the acromion (blue pins) including the (b, anteromedial view) coracoacromial ligament anteriorly (black arrow) towards the coracoid process (CP, green pin). Posteriorly (c, posterior view) it extends towards the posterior aspect of the acromion. The red pin marks the midpoint of the acromion. (d–f) The acromion has been resected and the roof of the subacromial bursa has been opened and reflected to expose its floor. Note its (d, superolateral view) medial‐lateral and anterior‐posterior dimensions (blue pins), (e, posterior view) posterior extent (white pins) over the infraspinatus tendon and (f, superior view) medial extent (white pins, blue latex from injection in situ) overlying the supraspinatus tendon/muscle in the supraspinous fossa. Abbreviations: A, anterior; GT, greater tubercle; I, inferior; L, lateral; M, medial; P, posterior; S, superior. Scale bar marked in cm
