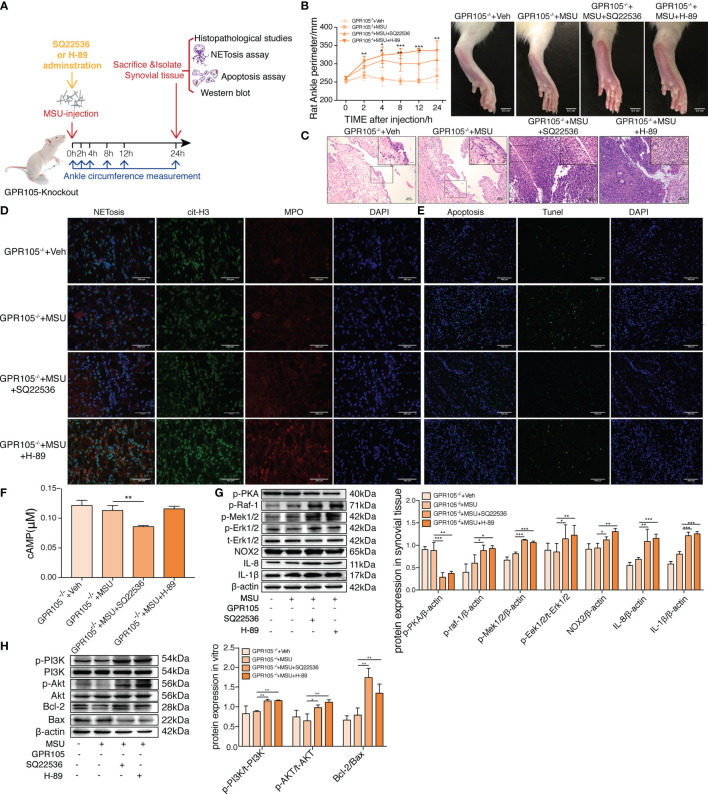
Figure 4.
Inhibition of cAMP-PKA pathway suppresses the effect of GPR105 knockout and switches apoptosis to NETosis in vivo. (A) GPR105−/− rats were intra-articularly injected with 5 mg/ml MSU to induce gouty arthritis. Rats were additionally treated with SQ22536 (100 μM), H-89 (10 μM), or DMSO as respectively indicated (n = 4). (B) The ankle perimeter at 0, 2, 4, 8 12, and 24 h after MSU injection. The representative photograph of ankle at 8 h after the injection of MSU. (C) Histologic analyses of synovial tissues at 24 h after MSU injection. (D) Representative images of synovial tissues infiltrating neutrophils (MPO, red) and presence of NETs (cit-H3, green). (E) Representative images of apoptosis cell (TUNEL, green) in synovial tissues. (F) The concentration of intracellular cAMP in synovial tissue of GPR105−/− rats 24 h after intra-articularly injected with Veh or MSU (5 mg/ml). (G) Western blot analysis and relative quantification of NETosis-related proteins in synovial tissues. (H) Western blot analysis and relative quantification of apoptosis-related proteins in synovial tissues. All representative blots are shown from four independent experiments. All values are presented as the mean ± SD (* p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001 versus corresponding GPR105−/−+MSU group, one-way ANOVA).