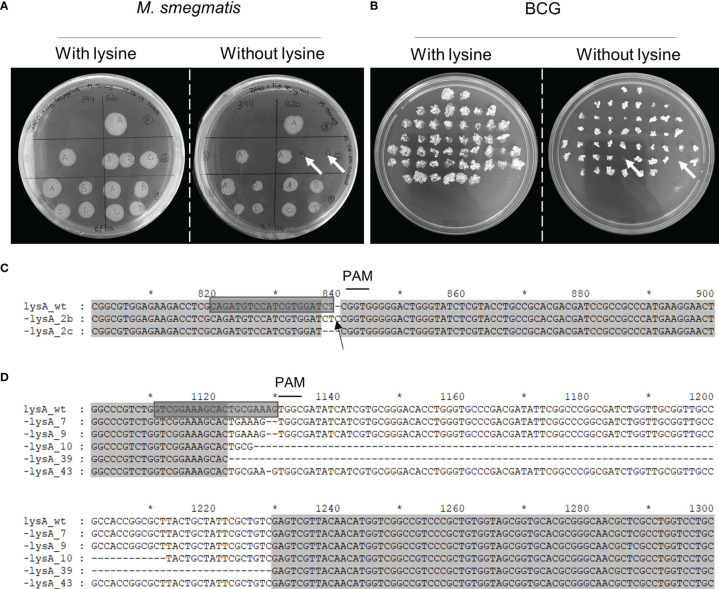
Figure 4.
Phenotypic screening and genotypic characterization of SmegΔlysA and BCGΔlysA. After the induction of Cas9, the cultures were seeded on lysine-supplemented plates to recover all viable bacteria. The colonies of (A) M. smegmatis, and (B) BCG were then seeded on mirror plates with and without lysine. The colonies that did not grow on plates without lysine (white arrows) indicate a positive knock-out. The lysA genes from (C) SmegΔlysA, and (D) BCGΔlysA were sequenced and compared to the wild-type sequence. The sgRNA used to target lysA is highlighted (grey box); the deleted nucleotides are represented by the dashed line; the inserted nucleotide is pointed out with a black arrow and the PAM site (NGG) is indicated with a line above. Numbering and asterisks represent the nucleotide positions regarding the full lysA gene sequence.