Figure 3.
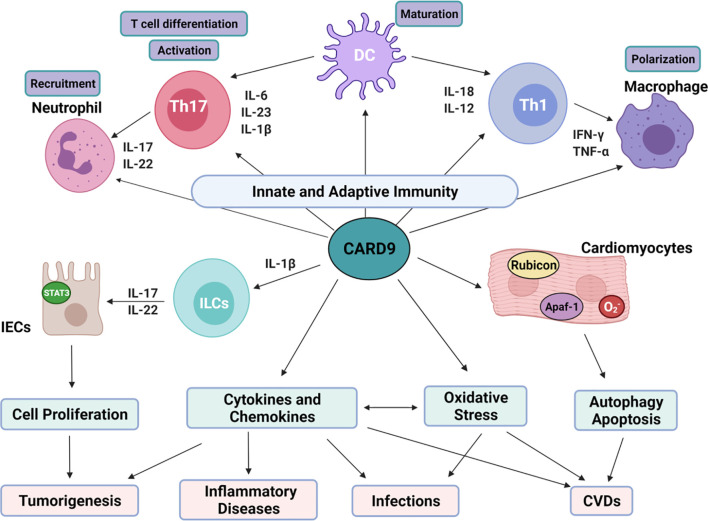
Overview on the role of CARD9 and relations with various diseases. CARD9-mediated cell proliferation, cytokines/chemokines production, oxidative stress, autophagy and apoptosis is critical for tumorgenesis, infections, inflammatory diseases and CVDs. (1). CARD9-mediated cytokines production interacts with innate and adaptive immunity. IL-6, IL-23 and IL-1β are essential for Th17 cell differentiation. IL-17 and IL-22 produced by Th17 cells trigger neutrophil recruitment. IL-12 and IL-18 from myeloid cells stimulate Th1 cell differentiation. IFN-γ released from Th1 then mobilizes and activates macrophages. The activated neutrophils and macrophages can further enhance Th1/Th17 differentiation and anti-fungal mechanisms. (2). CARD9 promotes the growth of IECs through interaction with ILCs. IL-1β from myeloid cells activates ILCs, leading to the release of IL-17 and IL-22 through CARD9-dependent signaling. After binding to its receptor on IECs, IL-22 activates STAT3, promoting IECs regeneration physiologically and tumor generation pathologically. (3). CARD9 can be activated by oxidative stress directly and indirectly. There’s crosstalk between ROS and cytokines prosunction. In cardiomyocytes, CARD9 can bind with Apaf-1 to disassociate apoptosome complex to inhibit apoptosis. CARD9 can also interact with Rubicon to promote autophagolysosome formation.