Figure 5.
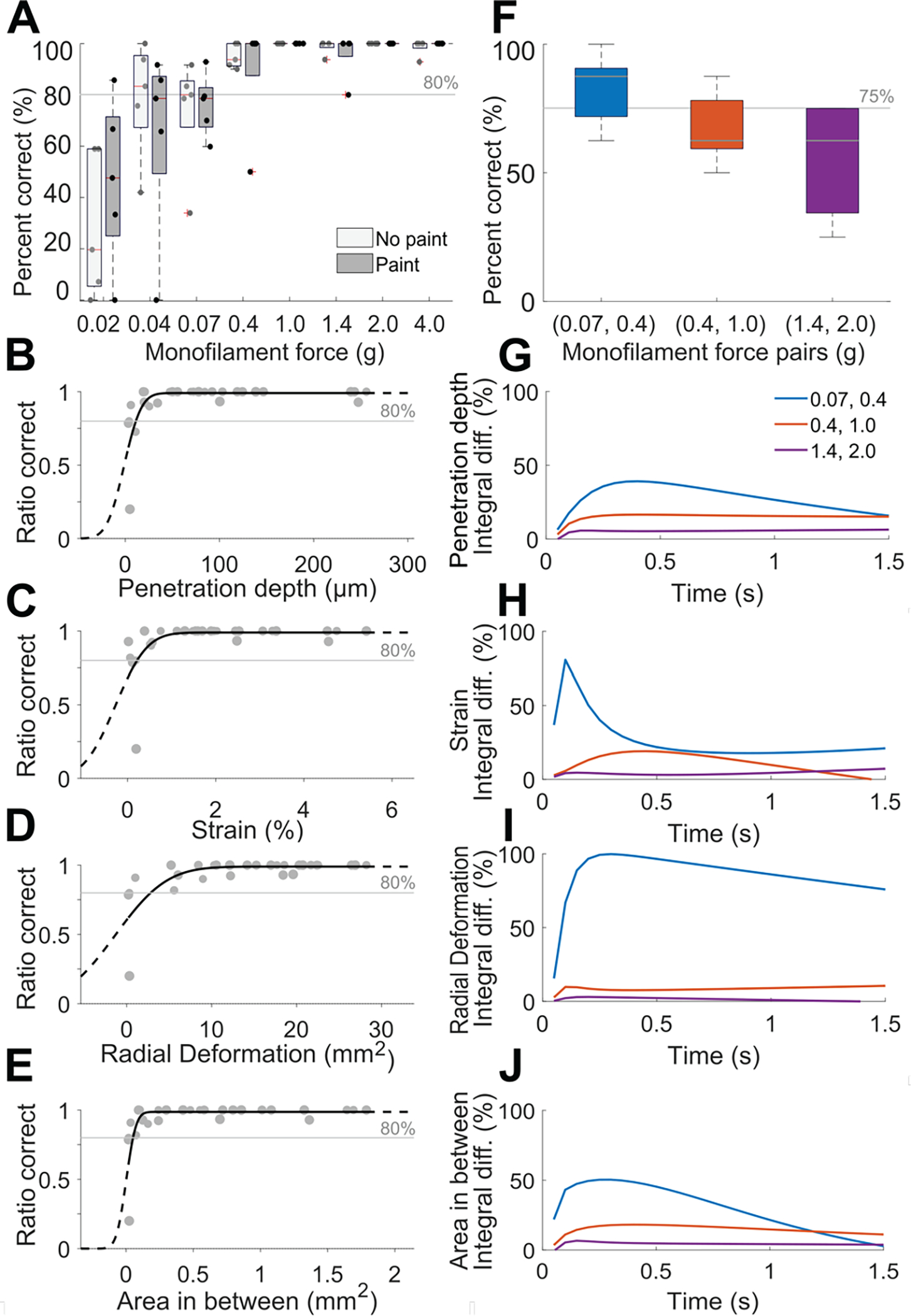
Results of psychophysical evaluation of absolute detection and discrimination threshold. (A) Absolute detection results showing average percent correct of trials in ascending and descending order in box whisker plots, where experiments conducted with and without paint on the finger pad skin yielded a negligible difference. (B)-(E) Psychometric plots depicting skin deformation of the five participants linked to their psychophysical results. (F) Discrimination results for pairs of monofilaments. For (A) and (F), N=5 participants, error bars in (F) show standard deviation. (G)-(J) Percent integral difference per metric between the three monofilaments pairs. Their ordering indicates a greater normalized difference for the smallest monofilament pair (0.07, 0.4 g) as compared to the other two pair, aligning with psychophysical results in panel (F).
