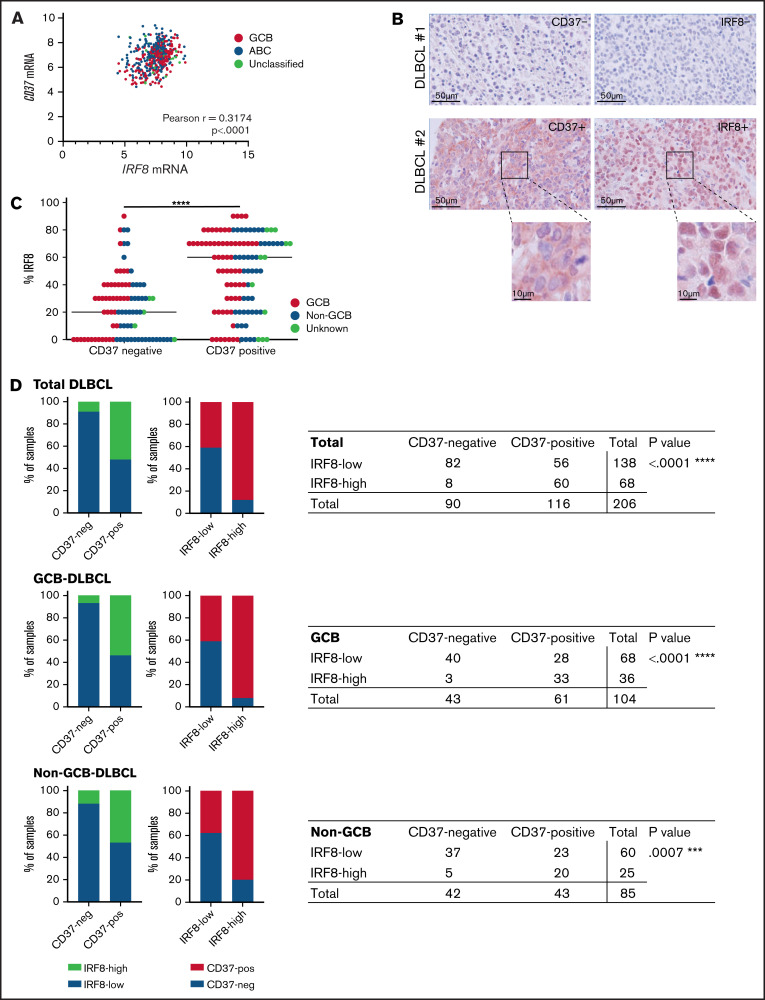
Figure 5.
IRF8 expression correlates with CD37 expression in primary human DLBCL. (A) Analysis of IRF8 and CD37 mRNA levels in primary DLBCL (n = 498). Linear regression R2= 0.1007. Pearson correlation r = 0.3174; 95% CI, 0.2361-0.3943; ****P < .0001. (B) CD37 and IRF8 IHC staining (red) of 2 representative DLBCL biopsies: CD37/IRF8 double-negative (top) and CD37/IRF8 double-positive (bottom) human DLBCL. Cell nuclei were counterstained with hematoxylin (blue). (C) IHC staining of CD37 and IRF8 was scored in 206 primary DLBCL samples. The percentage indicates the percentage of IRF8-positive tumor cells per sample. Each dot represents 1 tumor sample. GCB/non-GCB status was known for 189 samples and is indicated (red: GCB; blue: non-GCB). The bar indicates the median percent IRF8 value per group. χ-square test of the absolute number of total DLBCL samples per group showed a significant association between the percentage of IRF8 and CD37 expression. ****P < .0001. (D) Samples were determined CD37-negative and IRF8-low when scoring was <10% and <60%, respectively. Data about GCB (middle) and non-GCB (bottom) status were available for 189 out of the 206 analyzed patients. P value shows the statistical significance obtained using Fisher’s exact test. ****P < .0001 (total DLBCL), ****P < .0001 (GCB), and ***P = .0007 (non-GCB).