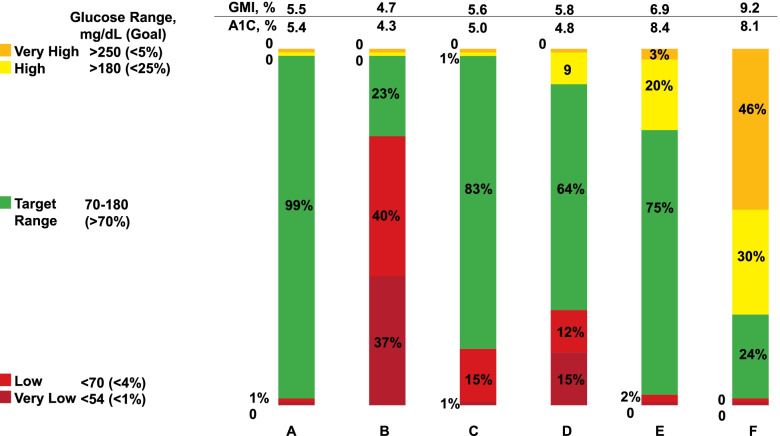
Fig. 1.
Time in range results from continuous glucose monitoring in patients with chronic kidney disease. Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) data from 6 individuals, including one person without diabetes (A) and five persons with diabetes and end-stage kidney disease (B–F), are presented. The CGM data are categorized as time-in-range, based on consensus recommendations. Glucose management indicator (GMI) is calculated from the average glucose results for each person, and lab-measured A1C is also presented. Note that significant variability in the glucose time-in-range is present within the same range of A1Cs (A–D and E, F). For example, for person E with an A1C of 8.4%, the GMI is 6.9%, and the CGM time-in-range is within acceptable limits. However, for person F, the A1C is 8.1%, GMI is 9.2%, and the CGM time-in-range is unacceptably high