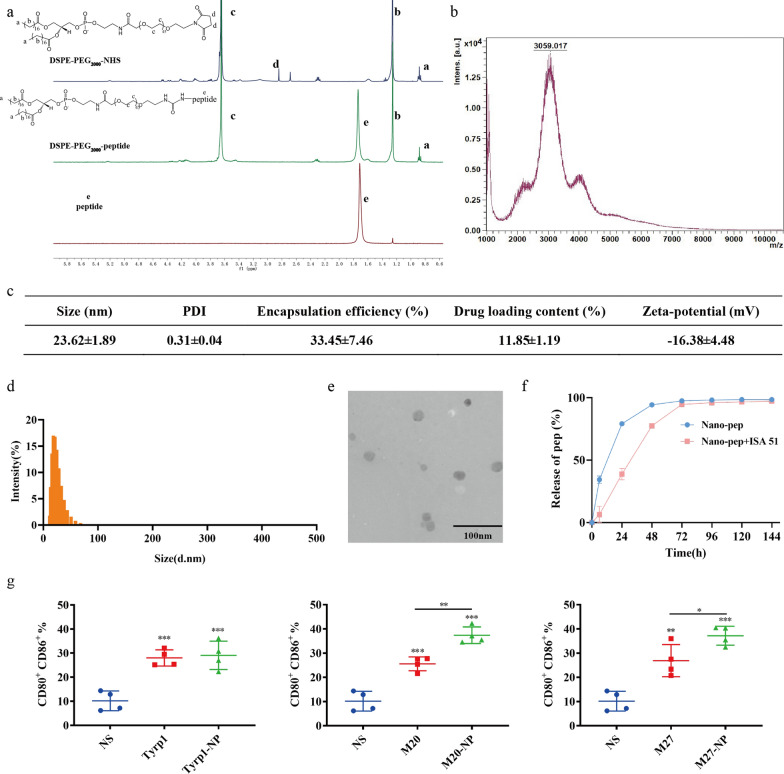
Fig. 2.
Characterization and in vitro DC-activation of neoantigen nanovaccines. a 1H NMR of DSPE-PEG2000-NHS (vehicle), DSPE-PEG2000-peptide and peptide (peptide: M27). b MALDI-TOF–MS of DSPE-PEG2000-peptide (peptide: M27). c Size, PDI, encapsulation efficiency, drug loading content and zeta-potential of nanovaccines. d Size of nanovaccines. e The transmission electron microscopy (TEM) image of nanovaccines. f Curves of peptide (M27) release from nanovaccines in different solutions. g Proportion of mature DC (CD11c+CD80+CD86+) after incubation with normal saline (NS), peptide (Tyrp1, M20 or M27) or nanovaccines (Tyrp1-NP, M20-NP or M27-NP) for 48 h. P-values were determined by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. **P = 0.0026 (M20 vs M20-NP), **P = 0.0029 (NS vs M27), *P = 0.0429 (M27 vs M27-NP), ***P < 0.001