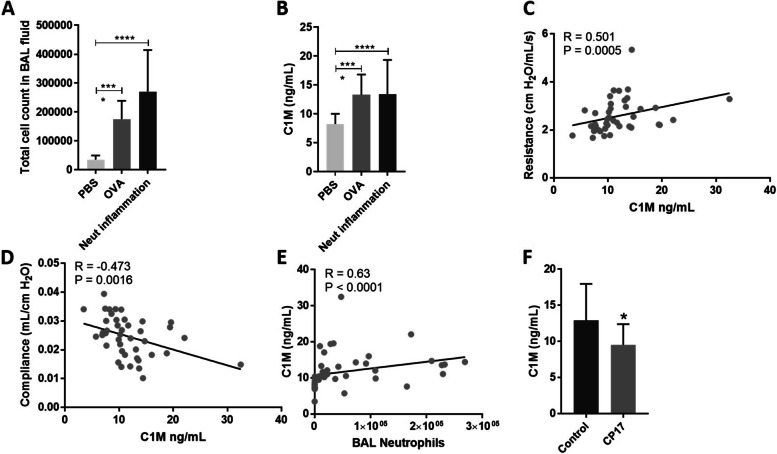
Fig. 6.
A Total cell count in the bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) were significantly increased in OVA mice and acute neutrophilic inflammation compared to control (P < 0.0001, P < 0.0001), respectively B Serum C1M was significantly increased in serum from OVA mice and mice with an acute neutrophilic inflammation as compared to controls (P < 0.0001, P = 0.0002), respectively. C Correlation between serum C1M level and airway resistance (r = 0.501, p = 0.0005). D Correlation between serum C1M level and airway compliance (r = -0.473, P = 0.0016). E Correlation between serum C1M level and BAL neutrophil was not significant. F Serum C1M levels were decreased in OVA mice treated with CP17, a peptide inhibiting neutrophil accumulation, compared to OVA mice treated with a scrambled peptide (p = 0.047). Data are presented as bar graphs and analyzed using the Kruskal-Wallis test using Dunn’s multiple comparisons or the Mann-Whitney test. The correlation was analyzed using spearman’s correlation. Asterisks indicate statistically significance: *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001 and ****p < 0.0001