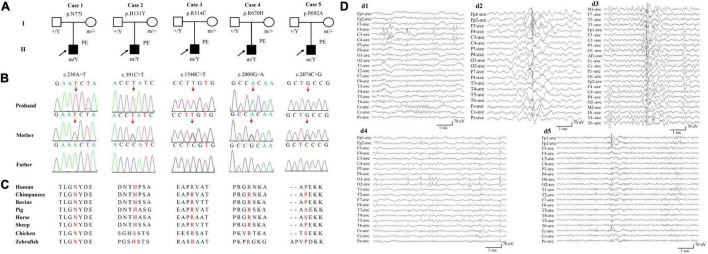
FIGURE 1.
Genetic and electroencephalograms (EEG) of the cases with AFF2 mutations. (A) Pedigrees of the five cases with AFF2 mutations and their corresponding phenotypes. PE, partial epilepsy. (B) DNA sequence chromatogram of the AFF2 mutations. Arrows indicate the positions of the mutations. (C) The amino acid sequence alignment of the five missense mutations shows that residues N77I, R514C, and R670H were highly conserved across various species. Residues H131Y and P692A were less conserved. (D) Changes of interictal EEG in the cases with AFF2 mutations. (d1) Interictal EEG of case 1 showed bilateral frontal-central spike and slow waves (obtained at the age of 8 years). (d2) Interictal EEG of case 2 showed bilateral frontal and anterior-temporal spike and slow waves (at the age of 9 years). (d3) Interictal EEG of case 3 showed spike and slow waves predominant at left hemisphere (at the age of 5 years). (d4) Interictal EEG of case 4 showed sharp waves predominant at bilateral occipital regions (at the age of 3 years). (d5) Interictal EEG of case 5 showed spike and slow waves predominant at bilateral frontal regions (at the age of 17 years).