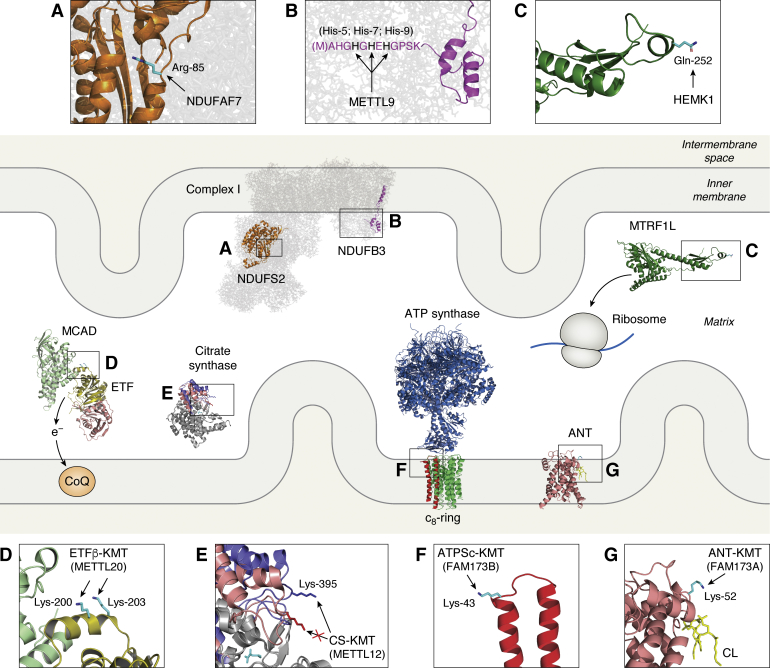
Figure 2.
Overview of mitochondrial protein MTases and their substrates. Shown are the substrates of known human mitochondrial protein MTases, as well as their submitochondrial localization and the specific residues targeted. A and B, the target site(s) of NDUFAF7 on NDUFS2 (A) and METTL9 on NDUFB3 (B) are shown on the Complex I structure (generated from pdb: 5LNK). The sequence in (B) represents the N-terminal region of bovine NDUFB3, which was demonstrated to contain methylhistidines at positions 5, 7, and 9 (47). C, the methylation site in MTRF1L targeted by HEMK1 is visualized on a model generated by AlphaFold and retrieved from UniProt (ID: AF-Q9UGC7-F1). D, the methylation sites for ETFβ-KMT in ETFβ (olive green) is found in a part interacting with MCAD (light green) (adapted from ref. (24)). CoQ, coenzyme Q; e-, electron. E, Lys-395 in citrate synthase (CS) is methylated by CS-KMT only when the enzyme is in the “open” conformation (blue), but not in “closed” conformation (red) with bound oxaloacetate (cyan) (adapted from ref. (68)). F, the c8-ring of ATP-synthase consist of eight ATPSc monomers, one of which is shown in red and magnified to visualize the methylation site (Lys-43) (adapted from ref. (84)). G, in the ANT structure, a cardiolipin molecule (CL; yellow) is bound in the vicinity of the methylation site (Lys-52) (adapted from ref. (92)). For some of the MTases, alternative names are given in parentheses. All structural visualizations were made using PyMOL Molecular Graphics System, Version 1.3 (Schrodinger, LLC). ETF, electron transfer flavoprotein; MTase, methyltransferase