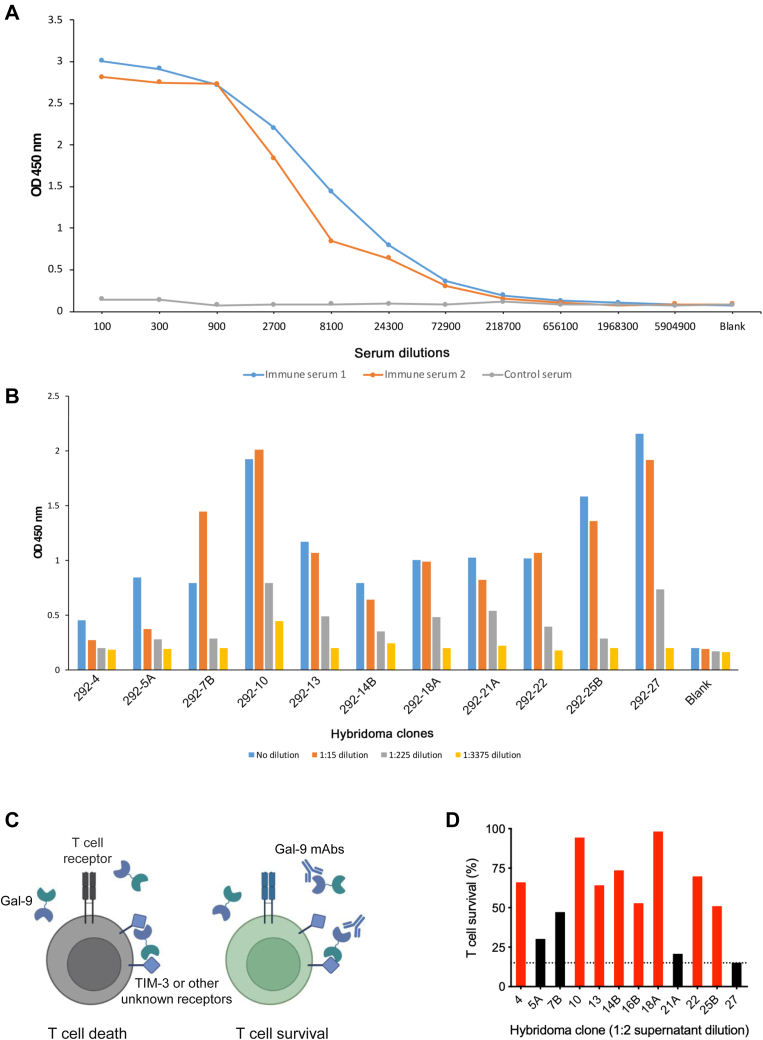
Figure 1.
Generation of Gal-9 mAbs.A, Gal-9 antiserum titration by ELISA. Two BALB/c mice were immunized with human Gal-9 protein. After the third immunization, serum was obtained, serially diluted, added to the plate immobilized with Gal-9 protein, and analyzed by ELISA. B, titration of hybridoma supernatants by ELISA. Supernatants from various antibody clones were serially diluted, added to the plate immobilized with Gal-9 protein, and analyzed by ELISA. C, schematic diagram of neutralizing Gal-9 antibodies to prevent Gal-9-induced T-cell death. Gal-9 crosslinks TIM-3 or other unidentified receptors with its N-terminal and C-terminal CRDs to induce T-cell death (left); Gal-9-neutralizing antibodies disrupt such crosslinking and inhibit Gal-9-induced T-cell death (right). D, analysis of T-cell survival by MTS assay. T cells were incubated overnight with 2 μg/ml Gal-9 in the presence of indicated hybridoma supernatants. Cell survival in the absence of Gal-9 was considered as 100%. Dashed line denotes cell survival when control supernatant was used. Red columns represent the hybridoma clones selected for the following experiments, and the black ones represent the clones not selected. CRD, carbohydrate-recognition domain; Gal-9, galectin-9; mAb, monoclonal antibody; MTS, 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-5-(3-carboxymethoxyphenyl)-2-(4-sulfophenyl)-2H-tetrazolium; TIM-3, T-cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain–containing molecule 3.