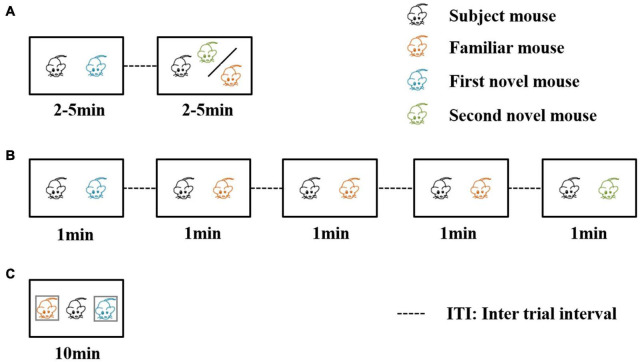
FIGURE 2.
Three behavioral paradigms for evaluating social recognition memory. In the first two of the three paradigms, a familiar mouse means the social stimulus the subject mouse has met in the previous trials. In the third paradigm, a familiar mouse refers to a cage mate of the subject mouse. (A) The direct interaction paradigm includes two encounters. The social stimulus the subject mouse meets in the second encounter can be familiar or novel. (B) The social habituation-dishabituation paradigm includes five trials of encounters. In the fifth trial, the subject mouse meets a novel social stimulus. (C) The social discrimination paradigm includes one encounter trial. The subject mouse meets two social stimuli at the same time. One is a familiar cage mate, and the other is a novel stimulus.