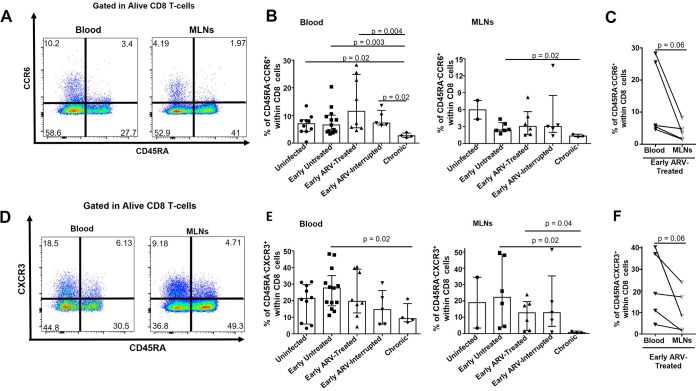
FIG 2.
Effect of early ARV initiation on the expression of migration markers CCR6 and CXCR3 by memory CD8 T cells. (A) Gating strategy used in flow cytometry to define CCR6+ memory CD8 T cells in both whole blood and MLNs. (B) Percentages of CCR6+ memory CD8 T cells in both whole blood and MLNs. (C) Dynamics of CCR6+ memory CD8 T cells in matched blood versus MLNs of early ARV-treated animals. (D) Gating strategy used in flow cytometry to define CXCR3+ memory CD8 T cells in both whole blood and MLNs. (E) Percentages of CXCR3+ memory CD8 T cells in both whole blood and MLNs. (F) Dynamics of CXCR3+ memory CD8 T cells in matched blood versus MLNs of early ARV-treated animals. Statistical significance is indicated in the figures. Differences among five study groups were determined by nonparametric Mann-Whitney rank test for unpaired variables, while the Wilcoxon rank tests were used for paired variables in the early ARV-treated group. Sample size in cross-sectional analysis as follows: uninfected, n = 10 in blood and n = 2 in MLNs; early untreated, n = 13 in blood and n = 6 in MLNs; early ARV treated, n = 8 in blood and n = 6 in MLNs; early ARV interrupted, n = 5 in blood and n = 5 in MLNs; and chronic, n = 4 in blood and n = 3 in MLNs. Sample size in paired analysis, n = 5.