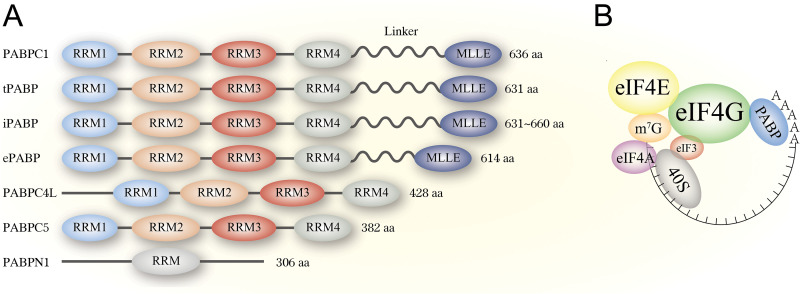
FIG 1.
The structure of PABPs and translation initiation complex in uninfected cells. (A) The structure of different human PABPs. PABP comprises N-terminus RRM domains, C-terminus MLLE domain, and a proline-rich linker sequence connect these two parts. PABPC5 and PABPN1 do not have MLLE and the linker region. (B) The translation initiation complex in uninfected cells. PABPs bind to poly(A) tail eukaryotic cellular mRNA, and they guide 3′-end of mRNA to its 5′ cap through interaction with eIF4G. eIF4G is a bridge between the PABP-poly(A) tail and 5′ cap, forming a head-to-tail loop and recruiting ribosome 40S subunit for further translation initiations.