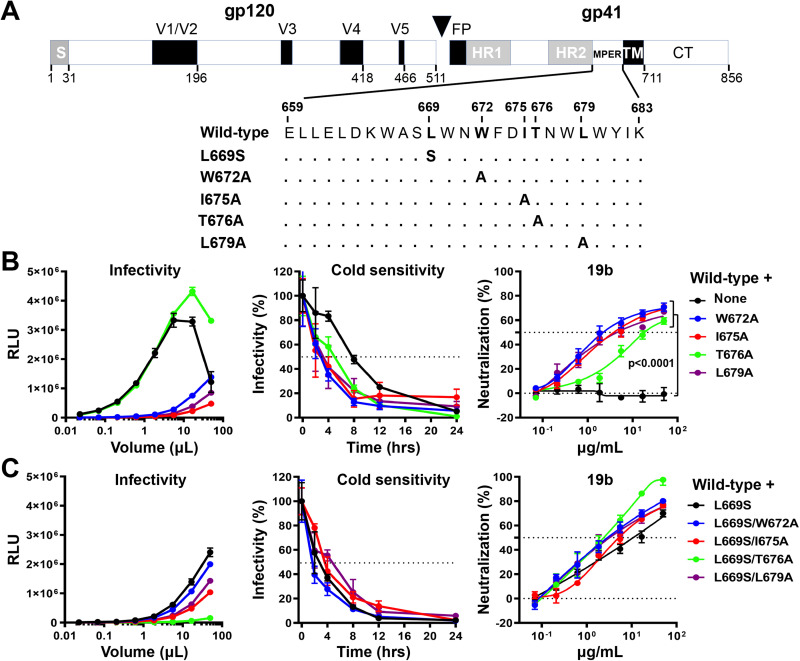
FIG 1.
Effects of MPER changes in the wild-type HIV-1AD8 Env. (A) A schematic representation of the HIV-1AD8 Env glycoprotein is shown with the gp120-gp41 cleavage site depicted as a black triangle. S, signal peptide; V1 to V5, gp120 hypervariable regions; FP, fusion peptide; HR, heptad repeat region; MPER, membrane-proximal external region; TM, transmembrane region; CT, cytoplasmic tail. The MPER amino acid changes studied herein are listed. Standard numbering of HIV-1 Env amino acid residues is used (140). (B and C) HEK293T cells were transfected with pNL4-3.Luc.R-E-vector and a plasmid expressing the wild-type or MPER-modified HIV-1AD8 Env. All Env mutants in C contain the L669S change either alone or in combination with the other MPER changes. Forty-eight hours later, the cell supernatants were collected, clarified, and added to TZM-bl cells in the presence of 20 μg/mL DEAE-Dextran. Forty-eight hours later, the infected cells were lysed, and the luciferase activity (in relative light units [RLU]) was measured as an indicator of virus infectivity (left). In the cold sensitivity assay, viruses were incubated on ice for the indicated times, after which the virus infectivity was measured (middle). In the neutralization assay with the 19b poorly neutralizing antibody, viruses were incubated with serial dilutions of 19b for 1 h at 37°C before TZM-bl cells were added and infectivity was measured. The results for cold sensitivity and 19b neutralization are normalized to those obtained in the absence of virus exposure to cold or the 19b antibody. The results shown are representative of those obtained in two independent experiments, expressed as means and standard deviations from triplicate luciferase readings. The significance of the difference in the sensitivity of the HIV-1AD8 Env variants to 19b neutralization was evaluated by a Student’s paired t test.