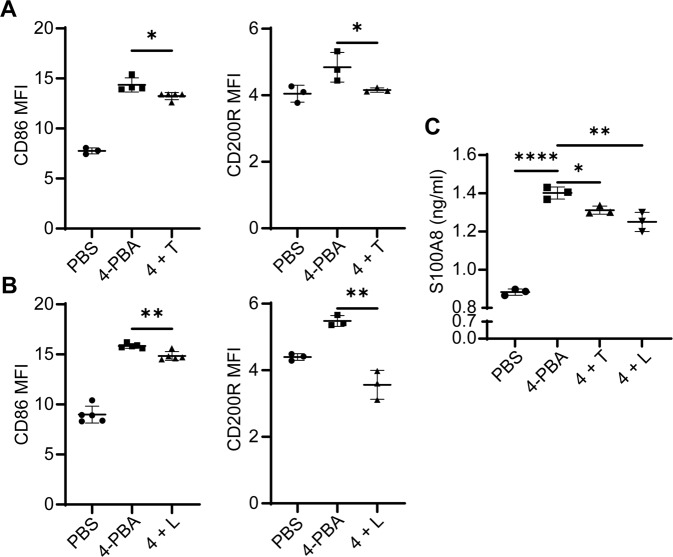
Fig. 5. Inhibition of PPARγ or STAT3 reduces the generation of resolving neutrophils by 4-PBA.
A Flow analyses of CD200R and CD86 levels on WT neutrophils treated with PBS, 4-PBA (1 mM; 24 hours) or pre-treated with T0070907 (0.5 µM) for 2 hours followed by 4-PBA (1 mM) stimulation for 24 hours (n = 3). B Flow analyses of CD200R and CD86 expression levels on WT neutrophils treated with PBS, 4-PBA (1 mM; 24 hours) or pre-treated with LLL12 (0.5 µM) for 2 hours followed by 4-PBA (1 mM) stimulation for 24 hours (n = 3). C ELISA analyses of S100A8 levels from WT neutrophils treated with PBS, 4-PBA (1 mM; 24 hours) or pre-treated with T0070907 (0.5 µM) or LLL12 (0.5 µM) for 2 hours followed by 4-PBA (1 mM) stimulation for 24 hours (n = 3). Data were plotted as mean ± SD. ** P < 0.01, * P < 0.05 using two-sided Student’s t test (A and B). ****P < 0.0001, ***P < 0.001, **P < 0.01, *P < 0.05 using one-way ANOVA test followed by the post-hoc Sidak multiple comparisons test (C). 4, 4-PBA; T, T0070907; L, LLL12.