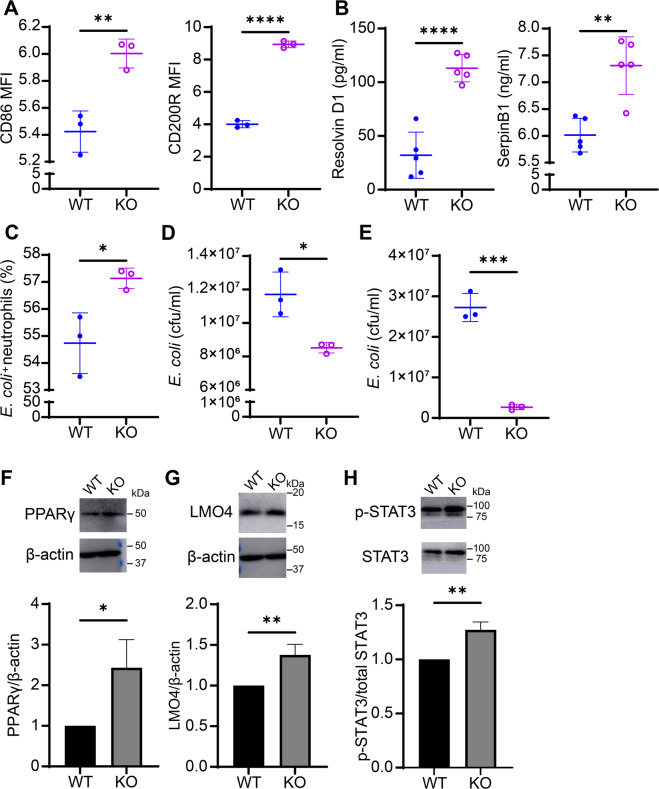
Fig. 6. Genetic deletion of TRAM renders constitutive generation of resolving neutrophils.
A Flow analyses of CD86 and CD200R expression levels on WT or TRAM KO neutrophils (n = 3). B The levels of Resolvin D1 and SerpinB1 from the supernatant of overnight-cultured WT or TRAM KO neutrophils (n = 3). C Flow analyses of neutrophil phagocytosis of GFP-labeled E. coli. Purified WT or TRAM KO neutrophils were co-incubated with GFP-labeled E. coli for 20 min. Following washing, neutrophils were subjected to flow analyses, and the percentages of GFP-E. coli containing neutrophils were counted and plotted (n = 3). D Analyses of bacterial killing through plating of viable E. coli harvested from lysed neutrophils. WT or TRAM KO neutrophils were co-incubated with GFP-labeled E. coli for 30 min. Following washing, neutrophils were lysed and plated on bacterial culture plates. The numbers of viable E. coli were counted and the CFU were plotted (n = 3). E Analyses of bacterial killing through plating of viable E. coli collected from culture supernatants. WT or TRAM KO neutrophils were co-incubated with GFP-labeled E. coli for 30 minutes. Culture supernatants containing extracellular viable bacteria were plated and counted with the CFU plotted (n = 3). F–H The levels of PPARγ, LMO4, β-actin, p-STAT3, total STAT3 of overnight-cultured WT or TRAM KO neutrophils were determined by Western blot. Data are representative of at least three independent experiments. Data plotted as mean ± SD. ****P < 0.0001, ***P < 0.001, **P < 0.01, *P < 0.05 using two-sided Student’s t test.