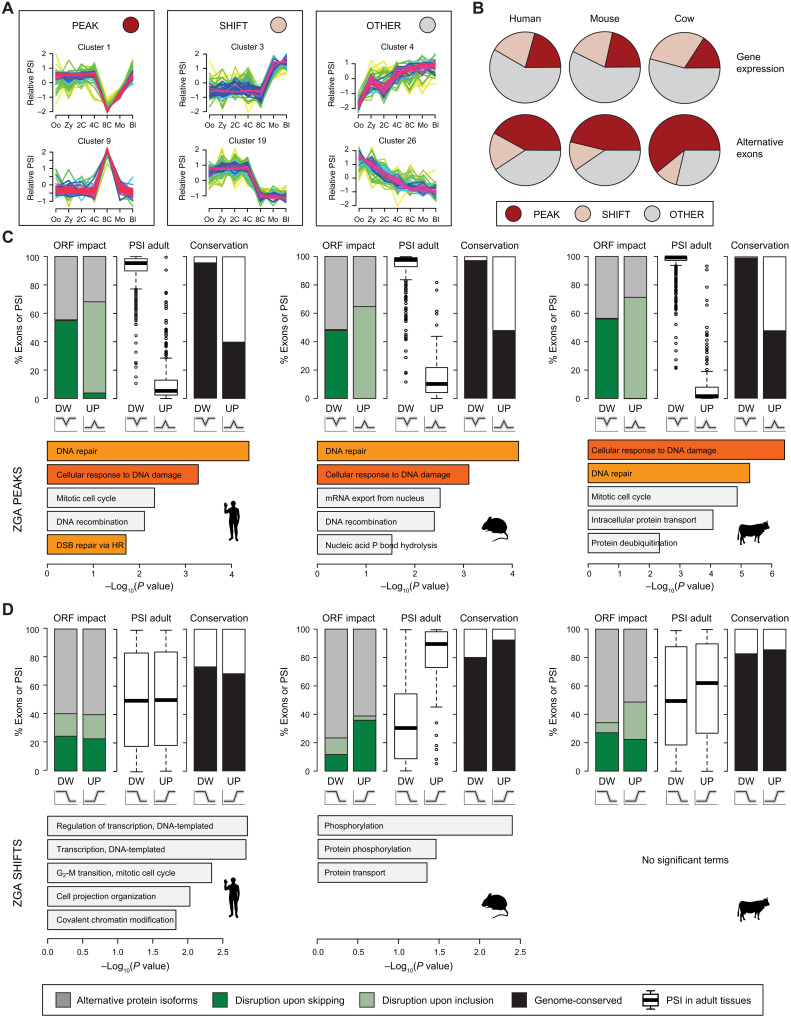
Fig. 2. Exons peaking at ZGA disrupt the ORFs and are enriched for DDR genes.
(A) Representative examples of the three main Mfuzz cluster types (Peak, Shift, and Other). (B) Proportions of each type of Mfuzz cluster for GE (top) and alternative exons with sufficient read coverage in all stages (bottom). (C and D) For each species, several features are shown for exons in Mfuzz clusters with Peak (C) or Shift (D) dynamics at ZGA, either with decreased (DW) or increased (UP) PSI. Top: Percentage of exons in coding sequences predicted to disrupt the ORF upon inclusion or skipping or to produce alternative protein isoforms (left), distribution of median PSIs in adult tissues (center), and percentage of exons with genomic conservation in any of the other two species (right). Bottom: Enriched Gene Ontology (GO) categories. Orange bars indicate DNA damage/repair–related categories. DSB, double-strand break.