Figure 1.
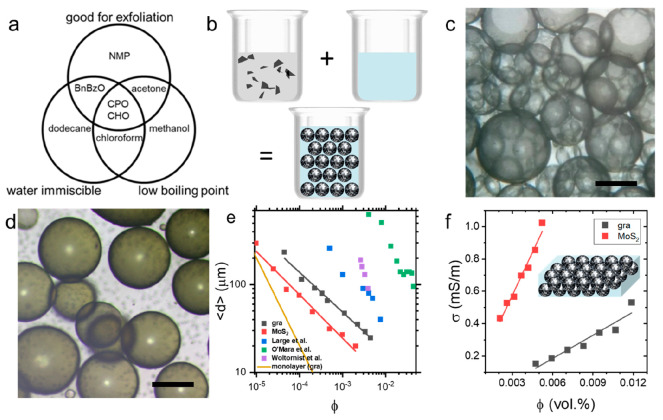
(a) Venn diagram illustrating solvent selection considerations for nanosheet-stabilized emulsions. (b) Schematic diagram of emulsification process where pristine few-layer nanosheets in a dispersion are homogenized with an immiscible liquid to form an emulsion and illustration of nanosheets on the surface of a droplet. (c) and (d) Optical micrographs of water-in-cycloketone droplets stabilized by graphene and MoS2, respectively; scale bar 100 μm. (e) Droplet diameter as a function of the nanosheet volume fraction for graphene and MoS2 emulsions showing a comparison to previous work and the minimum loading level defined by monolayer graphene. (f) Electrical conductivity of liquid emulsions as a function of nanosheet volume fraction for graphene/H2O/CHO and MoS2/H2O/CPO with an inset schematic of the droplet network.