FIGURE 2.
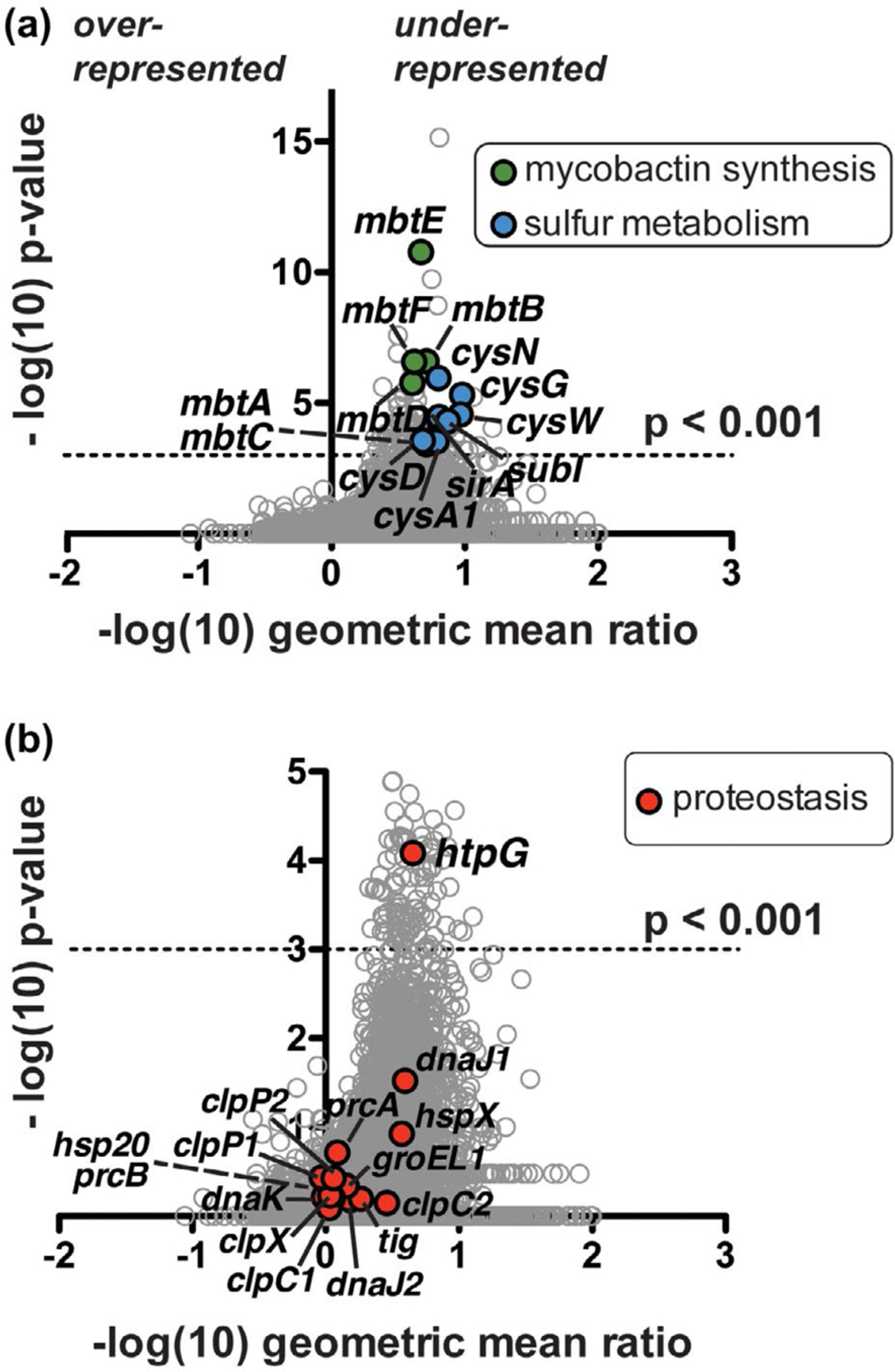
Tn-seq analysis suggests Mtb clpB function is related to oxidative stress response genes and a proposed protein chaperone-encoding gene, htpG. (a) Comparison of Mtb ΔclpB transposon library insertions to that of wild type. Each locus (circle) is plotted based on its p-value, determined by a Mann-Whitney U test, and fold change in sequence reads of the knockout relative to the wild-type background (Pritchard et al., 2014). Over 100 genes are significantly (p < .001) under-represented (right side of y-axis) in the ΔclpB background compared to the wild type; highlighted genes include mycobactin synthetic genes (mbt, green) and sulfur metabolism genes (blue), many of which have been linked to the oxidative stress response. (b) Enlarged representation of data from part A highlighting all annotated proteostasis genes (red), of which only the predicted chaperone gene htpG shows a significant genetic interaction with clpB
