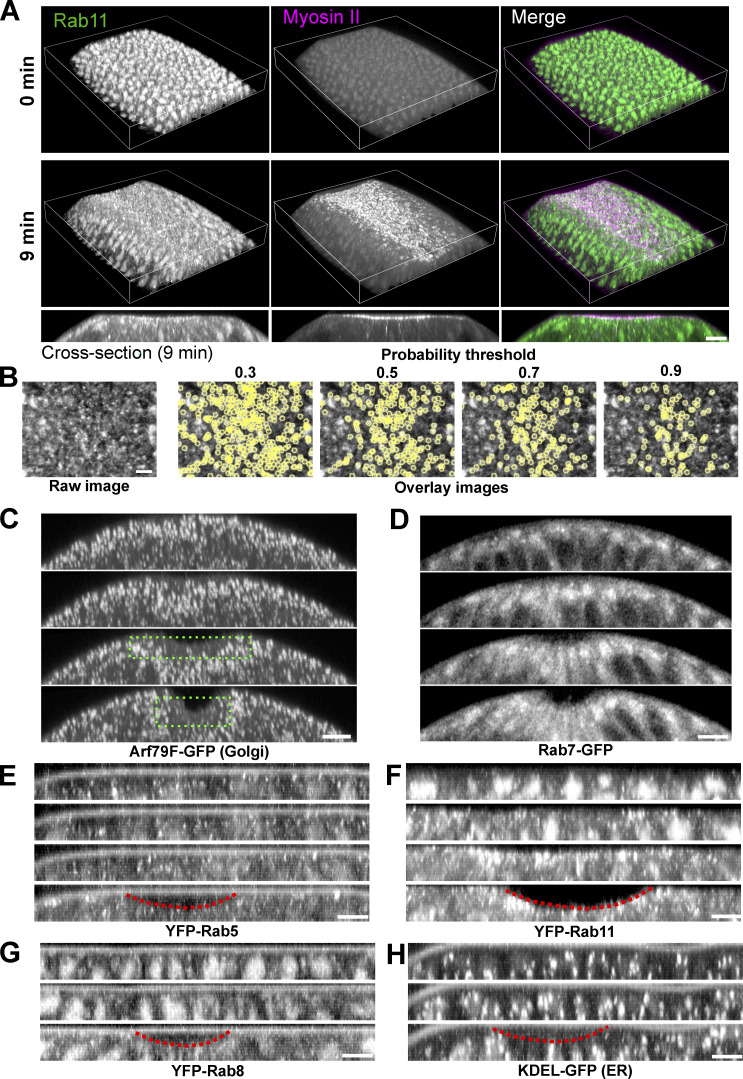
Figure S1.
Localization of Rab11 and other endomembrane compartments during ventral furrow formation. (A) 3D reconstruction of the ventral part of an embryo expressing YFP-Rab11 and mCherry-Sqh during ventral furrow formation showing apical accumulation of Rab11 vesicles in constricting cells. Magenta box indicates the apical region of the constricting cells. Bottom panel are the cross-section view images of the same embryo. Scale bar, 10 μm. (B) Vesicle segmentation using different probability threshold. Vesicles are segmented based on the probability map generated by ilastik. Threshold of 0.7 gives best quality of segmentation. (C–H) Localization change of different compartment markers in the ventral cross-section view of embryos. from late cellularization (top image in each panel) to early gastrulation. (C) Golgi marker Arf79F. Green dotted box shows the lack of Golgi puncta in the apical region of the constricting domain. (D) Late endosome marker Rab7. (E) Early endosome marker YFP-Rab5. (F) Recycling endosome marker YFP-Rab11. (G) YFP-Rab8. (H) ER marker KDEL-GFP. Among all the organelles examined here, Rab11 positive structures exhibit the most striking morphology and localization changes during ventral furrow formation. Images in A and B were taken on a multiphoton microscope. Scale bars, 10 μm. Images in C–F were taken on a spinning disk confocal microscope. Red dotted lines indicate the ventral furrow. Scale bars, 5 μm. The cross-section views were made by maximum intensity projection over 4–5 μm.