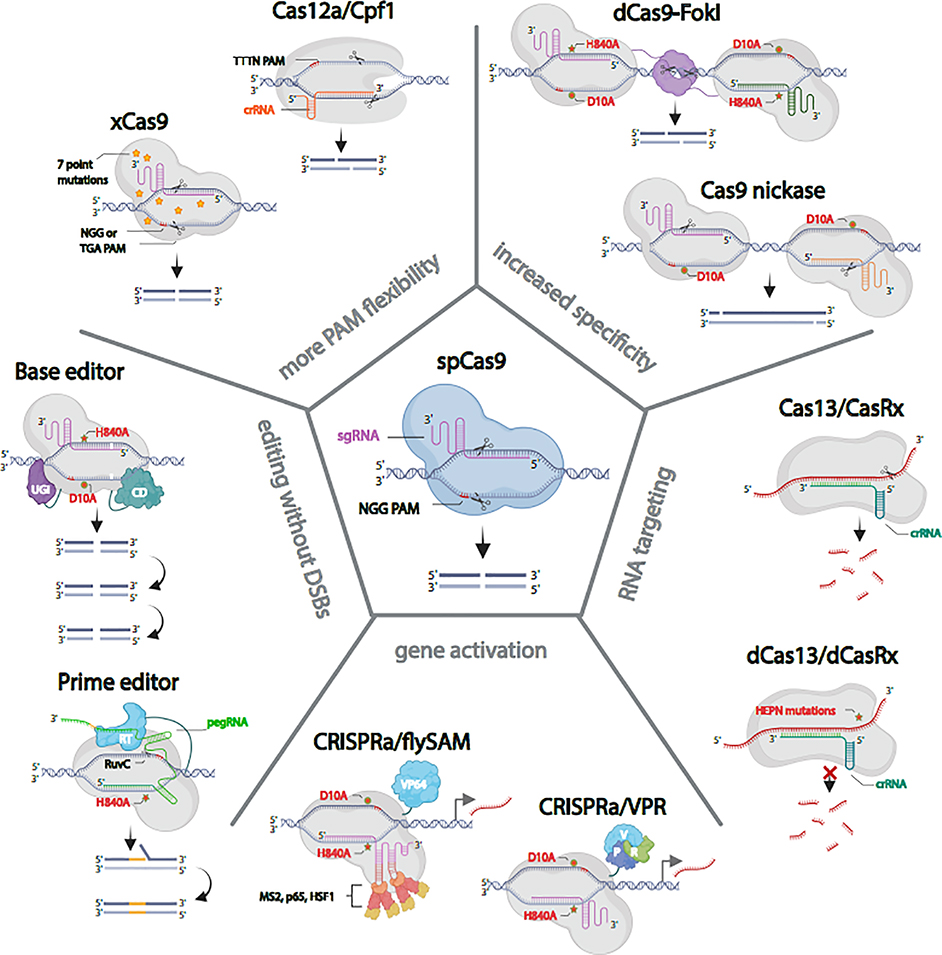
Figure 2. In vivo CRISPR in Drosophila with Cas9 and its alternatives.
spCas9, the most commonly used Cas protein in Drosophila produces reliable double strand breaks (DSBs). xCas9 and Cas12a/Cpf1 provide greater PAM flexibility. Paired Cas9 nickase and dCas9-FokI fusions minimize the possibility of off-target DSBs. A cytosine base editor (C>T, G>A) and prime editor allow for precise genome editing without making DSBs. dCas9-fused to VPR or synergistic activation mediator (SAM) produce robust gene activation in vivo. Cas13/CasRx binds and degrades target RNA. The catalytically inactive dCas13/dCasRx binds to RNA but does not cut it.