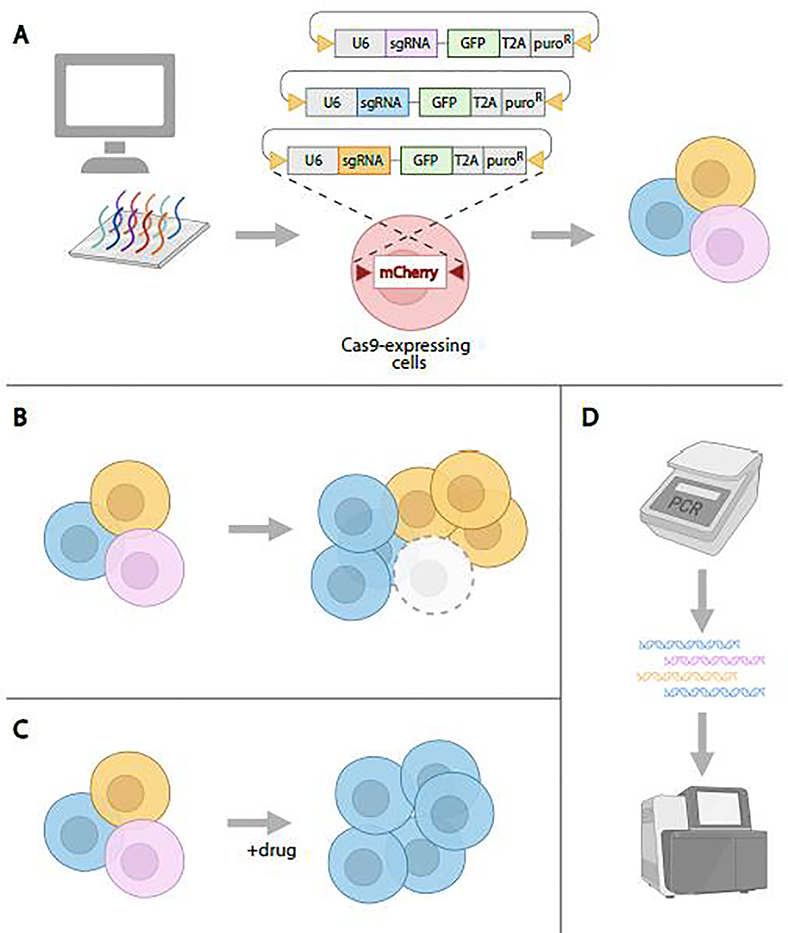
Figure 4. CRISPR pooled-format screening in Drosophila cultured cells.
A. To generate a pool of cells with knockout mutations, sgRNAs are designed and synthesized, then cloned into recombination mediated cassette-exchange (RMCE)-compatible expression vectors. Next, the sgRNA library plasmids are introduced into Cas9-expressing cells via RMCE, resulting in a population of cells in which sgRNAs are integrated into the genome, expressed, and generate knockouts via NHEJ. B. Outgrowth, followed by identification of sgRNAs that ‘drop out’ in the outgrown population as compared with the starting population, can be used to identify essential genes. C. Treatment of the cell population with a drug or other cytotoxin can be used to select for cells in which knockout confers resistance. Genes are identified by comparing sgRNAs in the treated population to sgRNAs in an untreated control. D. Following the pooled cell assay, genomic DNA is extracted and PCR is used to amplify sgRNA sequences. Next-generation sequencing and data analysis is then used to uncover the identity and proportion of sgRNAs in control and experimental knockout cell populations, followed by gene-level analyses.