Fig. 3.
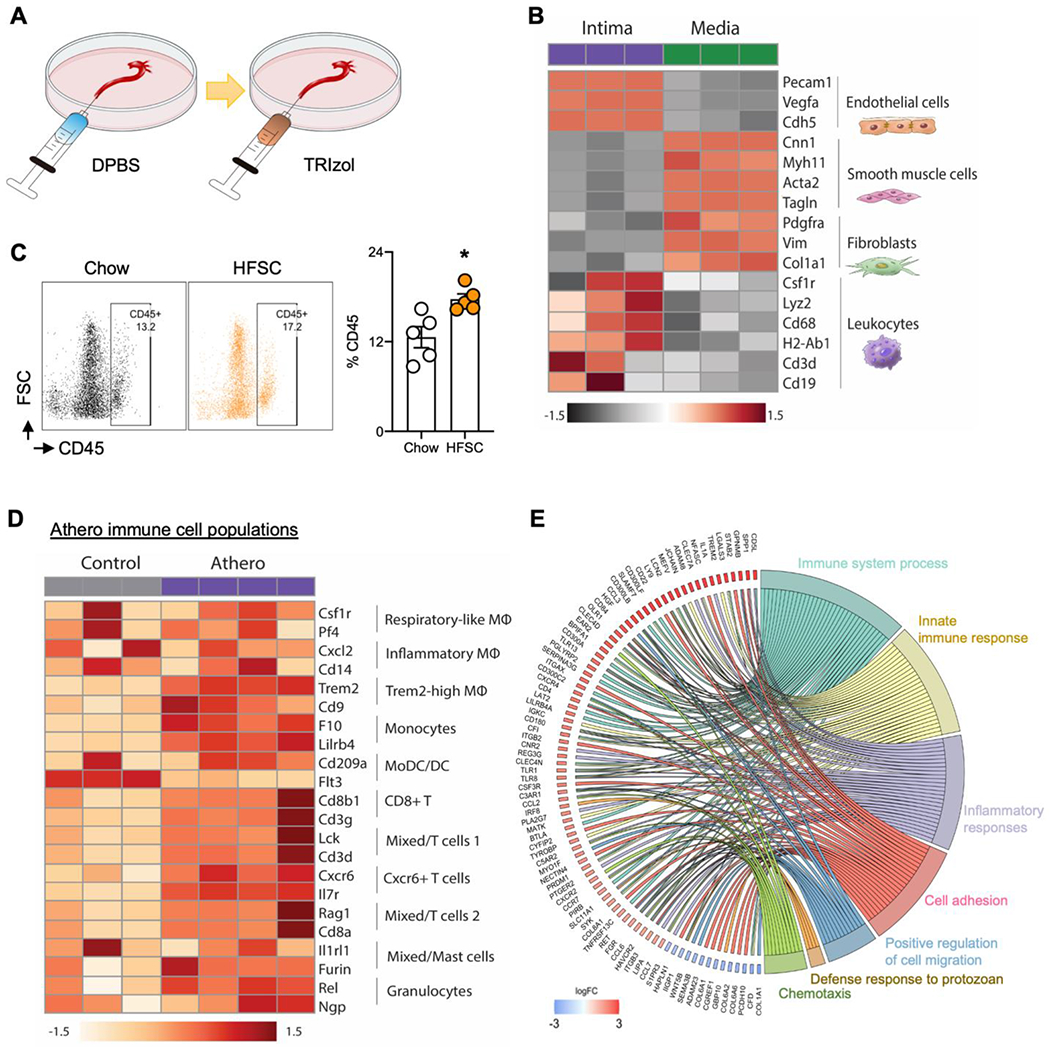
Intima peeling for isolation of mouse aortic intima and media alongside cell heterogeneity and gene enriched pathway analyses from control and HFSC atherosclerotic mouse aortas.
(A)Schematic illustration of intima peeling using TRIzol in aorta of eight-week-old C57BL/6 mice. (B) Heatmap showing differentially expressed aortic major cell marker genes in aortic intima and media by bulk RNA-seq analysis (FDR<0.05). (C) Flow cytometry showing the CD45+ leukocytes in comparison of aortic cell digestions from atherosclerosis (LDLR−/− mice fed with HFSC for 12 weeks) and chow diet controls. (D) Heatmap showing immune cells heterogeneity in atherosclerotic aorta (LDLR−/− mice fed with HFSC for 12 weeks) compared to chow control (FDR, <0.05). (E) GOChord plot showing the significantly regulated genes (log2 fold change, >1.5; FDR, <0.05) involved in the top 7 enriched pathways in the aortic intima from the HFSC atherosclerotic aorta and chow control.
