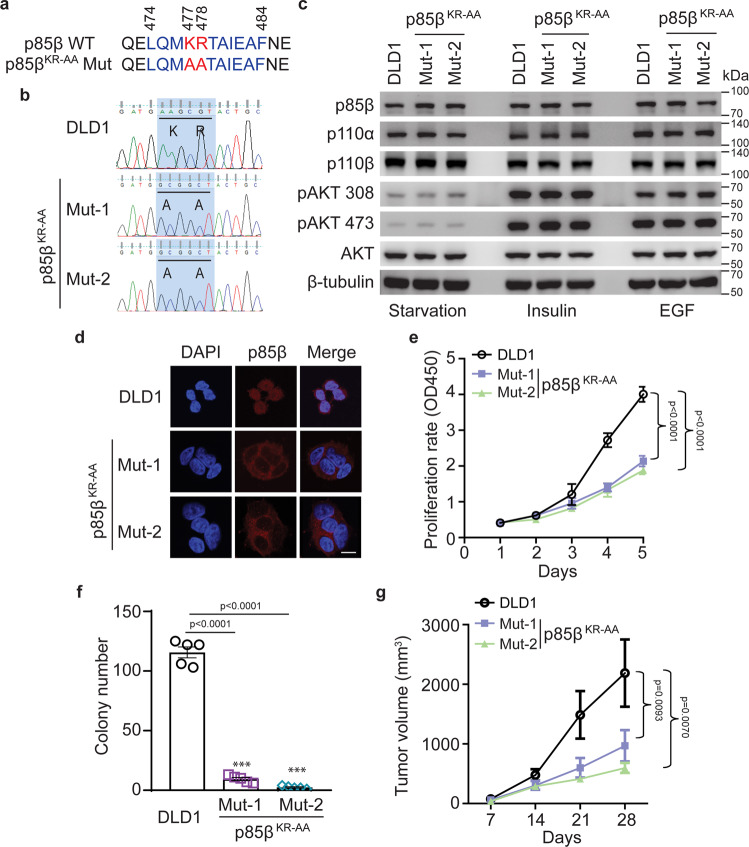
Fig. 4. Nuclear translocation of p85β is critical for the tumorigenicity of PIK3CA E545K mutant cells.
a A predicted Nuclear Localization Sequence (NLS) in p85β protein is highlighted in blue. The critical stretch basic amino acids K477R478 are highlighted in red. b Genomic DNA sequencing of DLD1 parental cells and K477A R478A mutant knock-in (p85βKR-AA) cells. c NLS mutation has no impact on p85β, p110α and p110β protein levels and AKT phosphorylation. Cells of the indicated genotypes were serum-starved, stimulated with insulin or EGF, and then lysed and blotted with indicated antibodies. d Cells of the indicated genotype were stained with an anti-p85β antibody. Mut-1 and Mut-2 are two independently derived p85βKR-AA mutant knock-in clones. e–g Cells of the indicated genotypes were assayed for cell proliferation (e), colony formation (n = 5) (f), and xenograft tumor growth (10 tumors/group) (g). Statistical analyses, two-way ANOVA was used for e, g, and student’s t-test (two-tailed) was used for f. Data are presented as mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. Source data are provided as a Source Data file. Scale bar = 10 µm.