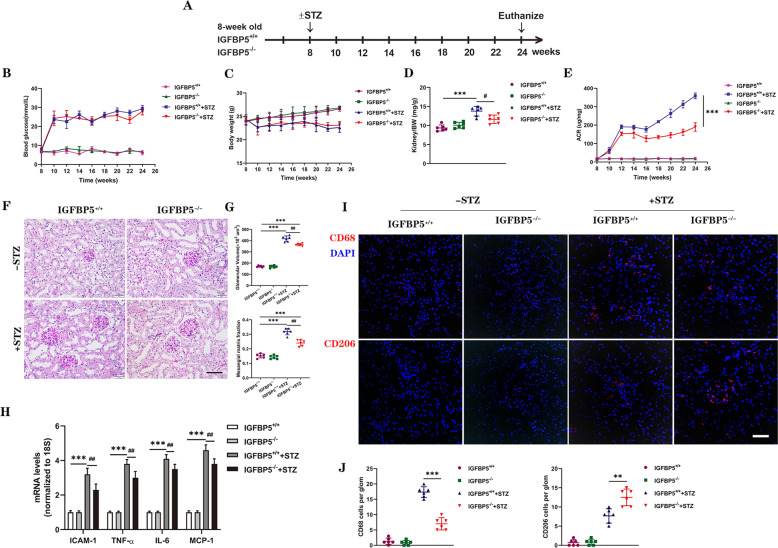
Fig. 2. IGFBP5 ablation protects against diabetic glomerulopathy.
A Schematic showing the experimental design. STZ or citrate buffer vehicle was injected into 8-week-old IGFBP5+/+ and IGFBP5−/− mice. The mice were euthanized at 16 weeks postinjection for analysis. n = 6 mice. B, C Biweekly blood glucose and body weight measurements of control and diabetic mice. D Kidney to-body weight (BW) ratio at 16 weeks after DM induction. E Urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratio (ACR) over time; n = 6 mice. F Representative images of periodic acid-Schiff (PAS)-stained kidneys. Scale bar, 50 μm. G Quantification of glomerular volume and mesangial matrix fraction per mouse; n = 6 mice. H RT–PCR analysis of the mRNA levels of ICAM-1, TNF-α, IL-6, and MCP-1 in control and diabetic mice. n = 6 mice. I Representative images of CD68 and CD206 immunofluorescence. Scale bar, 50 μm. J Quantification of CD68- and CD206-positive cells in diabetic and non-diabetic IGFBP5+/+ or IGFBP5−/− mice. The data are shown as the mean ± SD. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001; #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01.