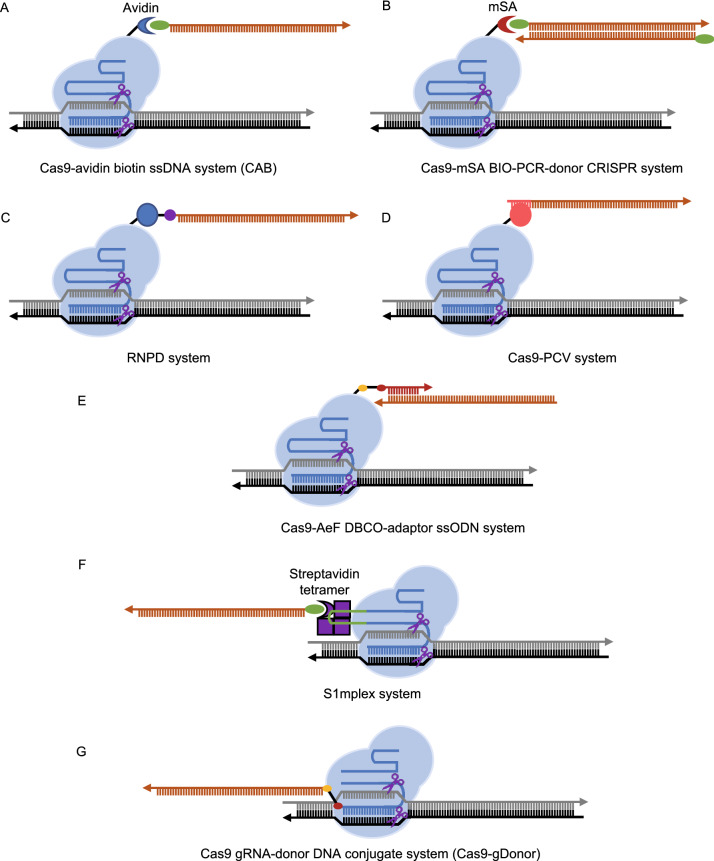
Figure 4. Different methods to recruit donor DNA to target site.
(A) Cas9-avidin biotin ssDNA (CAB) system. Biotin, green oval. (B) Cas9-mSA BIO-PCR-donor CRISPR system. mSA, monomeric streptavidin. (C) The ribonucleoprotein DNA (RNPD) system. SNAP peptide, blue circle. O6-benzylguanine (BG), purple circle. Covalent bond between SNAP peptide and O6-benzylguanine (BG), black line. (D) The Cas9-PCV system. PCV, porcine circovirus 2 Rep protein, is shown with pink circle. PCV recognition sequence, pink line. (E) Cas9-AeF DBCO-adaptor ssODN system. AeF, noncanonical amino acid 4-(2-azidoethoxy)-l-phenylalanine. Azide group of AeF, golden oval. DBCO, red oval. Adaptor, red line. (F) S1mplex system. Chimeric RNA, composed of gRNA and S1m aptamer, recruits biotin-labeled ssDNA donor to the target site by interacting with the streptavidin tetramer (purple box). S1m aptamer, green line. (G) Guide RNA donor DNA conjugate (gDonor) system. Azide group, golden oval. DBCO, red oval. gRNA, blue line. DNA donor, orange line. The direction of the arrow represents the 5′ to 3′ direction