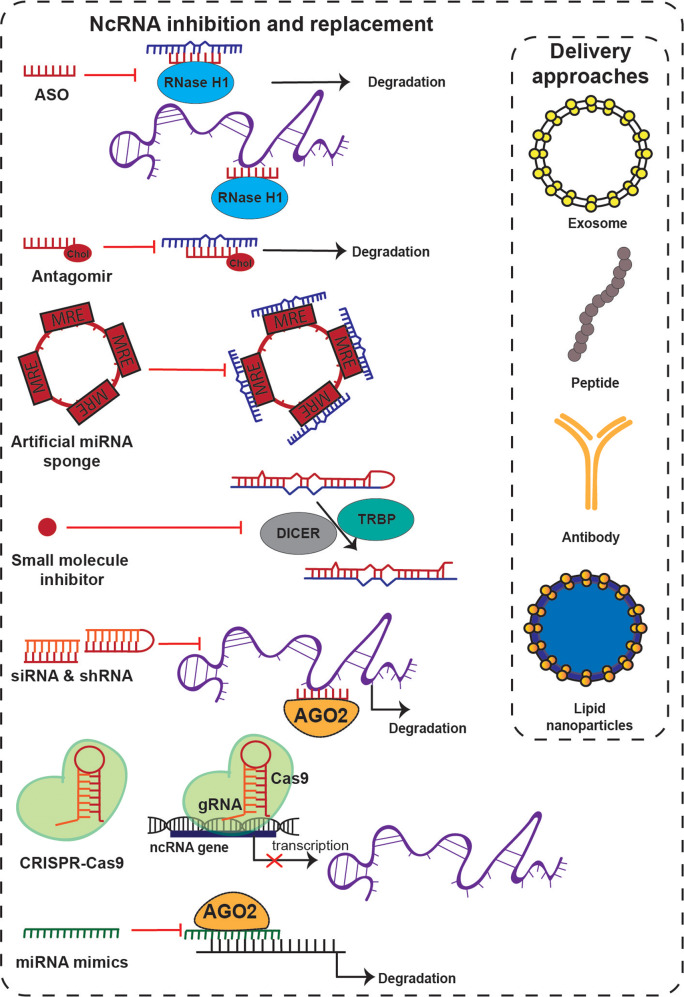
Fig. 3.
Therapeutic modalities to target ncRNAs. The therapeutic strategy to target overexpressed ncRNAs is to inhibit the specific ncRNA molecules. The inhibition modalities include (1) antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs): ASOs bind to complementary RNA sequences to block and inhibit their function and induce their degradation via RNAse-H-mediated cleavage; (2) antagomirs: antagomirs bind to complementary miRNAs and induce their degradation, thus preventing their interaction with target mRNA; (3) artificial miRNA sponges: artificial RNAs contain multiple high-affinity miRNA antisense binding sites that can sequester miRNAs from their target mRNAs; (4) small molecules: these molecules can interrupt any step of RNA transcription process; (5) small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) and short hairpin RNAs (shRNAs): these artificially synthesized double-stranded RNAs bind to complementary target ncRNA when loaded to AGO2, leading to the degradation of target RNA; (6) CRISPR/Cas9-based editing approaches, delivering the Cas9 nuclease complexed with a synthetic guide RNA (gRNA) to precisely cut the target ncRNA; and (7) miRNA mimics: miRNA mimics are used for replacing or substituting downregulated tumor suppressor miRNAs. Commonly used delivery systems of these ncRNA therapeutic modalities include lipid nanoparticles, exosomes, antibodies, and peptides.