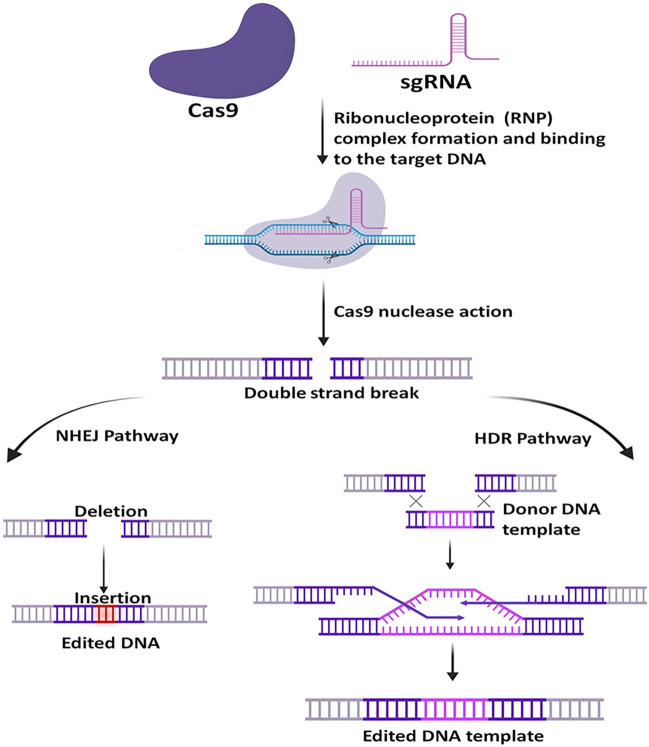
FIGURE 3.
General mechanism of CRISPR-Cas9. At first, the target-specific sgRNA forms complex with Cas9, then the active RNP complex binds with the specific target DNA and creates a double-strand break. Upon Cleavage, the DNA is repaired via two pathways, the non-homologous end-joining (NHEJ) pathway or the homology-directed repair (HDR) pathway. NHEJ is more frequent in nature and is error-prone, whereas the HDR requires a homology template and is less error-prone.