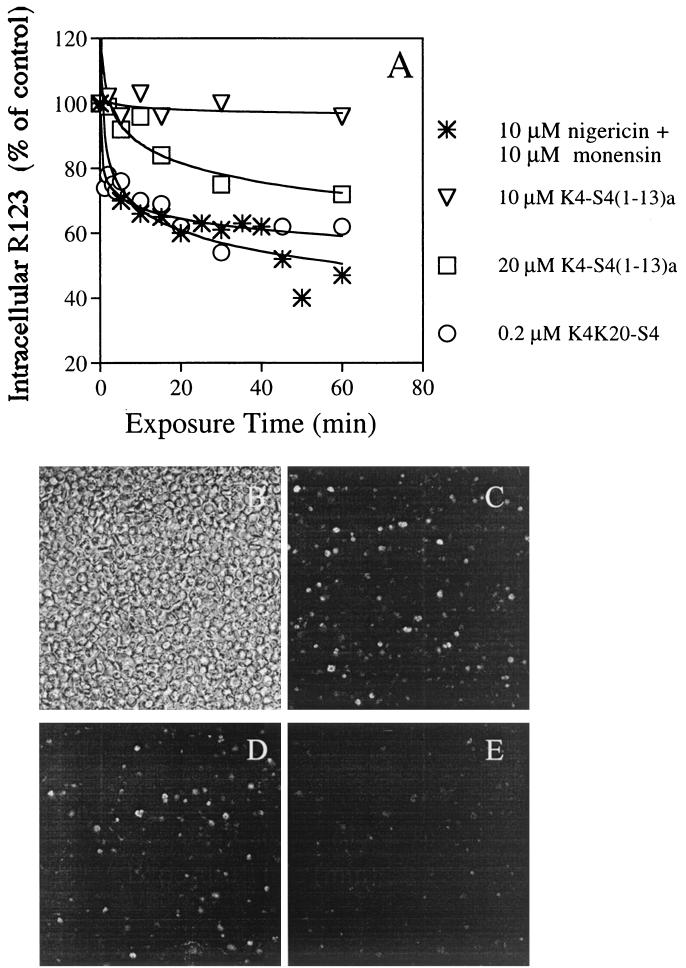
FIG. 7.
Dissipation of the membrane potential resulting in leakage of R123 from infected cells, as analyzed using fluorescence spectroscopy (A) and confocal microscopy (B to E). (A) Trophozoites (0.5% hematocrit) that were preincubated with R123 were exposed to peptides or to a mixture of nigericin and monensin to dissipate the ion gradients across membranes. Samples—taken at the indicated time intervals—were washed and resuspended in PBS, and their fluorescence was read (λex = 530 nm; λem = 585 nm). Relative fluorescence (as a percentage of that of the untreated control at the same time) was plotted against the time of incubation. Panel B shows the light transmission image of a microscope field of the R123 treated infected cells. Panels C, D, and E show single optical sections (rhodamine filter) of the same field, 1 to 2 min after addition of 0, 10, and 20 μM K4-S4(1–13)a, respectively.