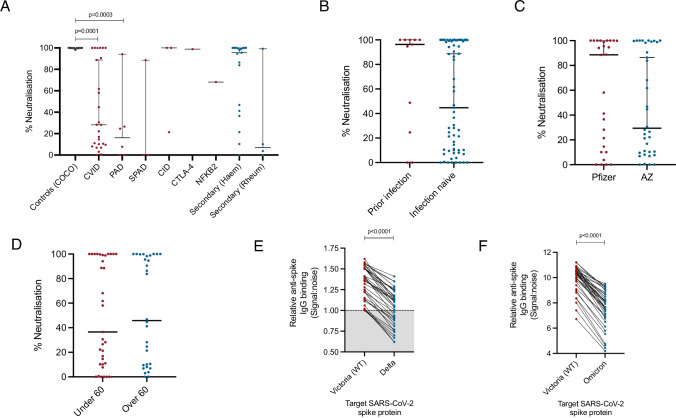
Fig. 4.
Functional immunity following SARS-CoV-2 vaccination in individuals with antibody deficiency. Serum neutralisation capacity was assessed using live virus neutralisation in seropositive individuals sampled 1–2 months post second vaccine dose. A Serum neutralising antibody capacity of seropositive individuals by underlying immunodeficiency. B Comparison of serum neutralising antibody capacity between individuals with prior PCR proven SARS-CoV-2 infection and those who were infection naive. C Comparison of serum neutralising antibody capacity between recipients of the Pfizer and AstraZeneca vaccinations. D Comparison of serum neutralising antibody capacity by age of participants. E Comparison of binding of vaccine-induced IgG antibodies from participants sampled 1–2 months post vaccination to the wild-type (Victoria) SARS-CoV-2 spike protein and the Delta variant of concern within an ELISA detection system. F Comparison of binding of vaccine-induced IgG antibodies from participants sampled 1–2 months post vaccination to the wild-type (Victoria) SARS-CoV-2 spike protein and the Omicron variant of concern within an ELISA detection system