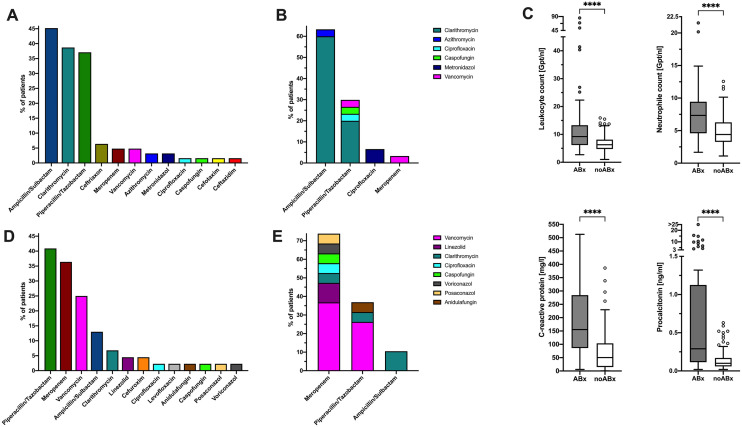
Fig. 1.
Antimicrobial use at primary admission and after transferral from other centres. A Antimicrobial substances and B combination therapies given as initial therapy at primary admission, n = 62 patients C Laboratory parameters of patients who received antimicrobial therapy at primary admission vs. patients who did not (medians): leukocyte count 9.23 (IQR 6.18–13.3) vs. 6.3 (IQR 4.76–8.13) Gpt/nl; neutrophil count 7.34 (IQR 4.6–9.44) vs. 4.41 (IQR 3.27–6.28) Gpt/nl; CRP 155.5 (IQR 68.1–284.38) vs. 50.45 mg/l (IQR 14.73–103.85); PCT 0.29 (IQR 0.12–1.125) vs. 0.1 µg/l (0.06–0.17); all p < 0.0001. D Antimicrobial substances and E) combination therapies given as initial therapy for transferred patients, n = 44 patients. A, B, D, E show the percentage of patients receiving the respective antimicrobial, leading to > 100% total because of dual or triple therapies. ABx antimicrobial therapy