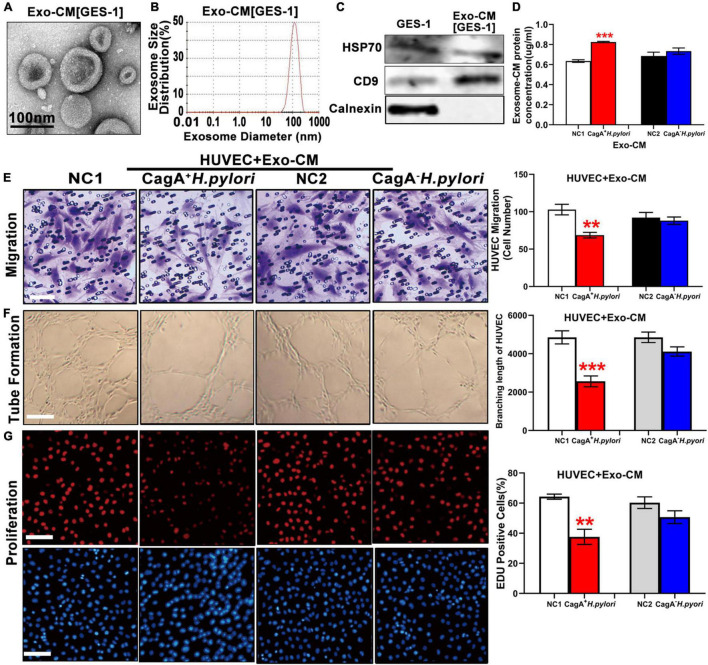
FIGURE 4.
Exosomes from conditioned medium of human gastric epithelial cells (GES-1) cultured with CagA+ H. pylori, not with CagA– H. pylori, impaired endothelial function in vitro. Exosomes from conditioned medium of GES-1 cultured with CagA+ H. pylori exhibited typical exosome morphology (A) and size distribution (B). Western blotting analysis confirmed the presence of exosomes markers (HSP70, CD9) and absence of calnexin in exosomes (C). Exosome protein concentration was significantly higher in the conditioned medium of GES-1 cultured with CagA+ H. pylori than that cultured with CagA– H. pylori (D). Treatment of HUVECs with exosomes-CM (100 ug/ml) from CagA+ H. pylori, not from CagA– H. pylori, infected GES-1 significantly inhibited the function of HUVECs with decreased migration (E, scale bars = 25 μm), tube formation (F, scale bars = 100 μm), and proliferation (G, scale bars = 100 μm). NC(1/2): normal control; GES-1: human gastric epithelial cells; HUVEC: human umbilical vein endothelial cell; Exo-CM: Exosomes from conditioned medium. Data are presented as mean ± SEM; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001 by t-test. Experiment was repeated 3 times for every measurement.