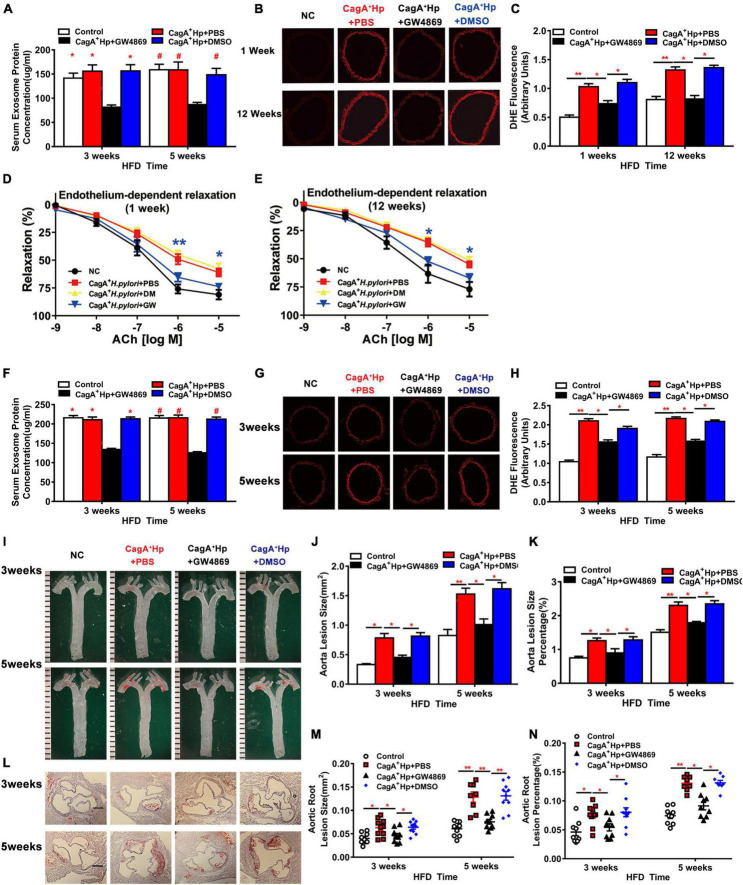
FIGURE 6.
Blocking exosomes release with GW4869 prevented endothelial dysfunction and atherosclerosis in mice with CagA+ H. pylori infection. Treatment with GW4869 significantly decreased the serum exosome level (A) and ROS formation in thoracic aorta (B–C) with improved ACh-induced aortic relaxation (D,E) (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, CagA+ H. pylori vs. CagA+ H. pylori + NAC by one-way ANOVA) in C57BL/6 mice with CagA+ H. pylori infection. GW4869 treatment also significantly decreased serum exosomes level in LDLR–/– mice with CagA+ H. pylori infection (F). After 3 or 5 weeks of high-fat diet (HFD), ROS formation (G,H) and atherosclerotic plaque formation in aorta and aortic root (I–N) were significantly increased in LDLR–/–mice with CagA+ H. pylori infection that were prevented with GW4869 treatment. NC: normal control; ACh: acetylcholine; CagA+ Hp: CagA+ H. pylori; DMSO: dimethylsulfoxide (solvent for GW4869). Data are presented as mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 by one-way ANOVA, N = 8–10 mice for each group at each time point.