Figure 1.
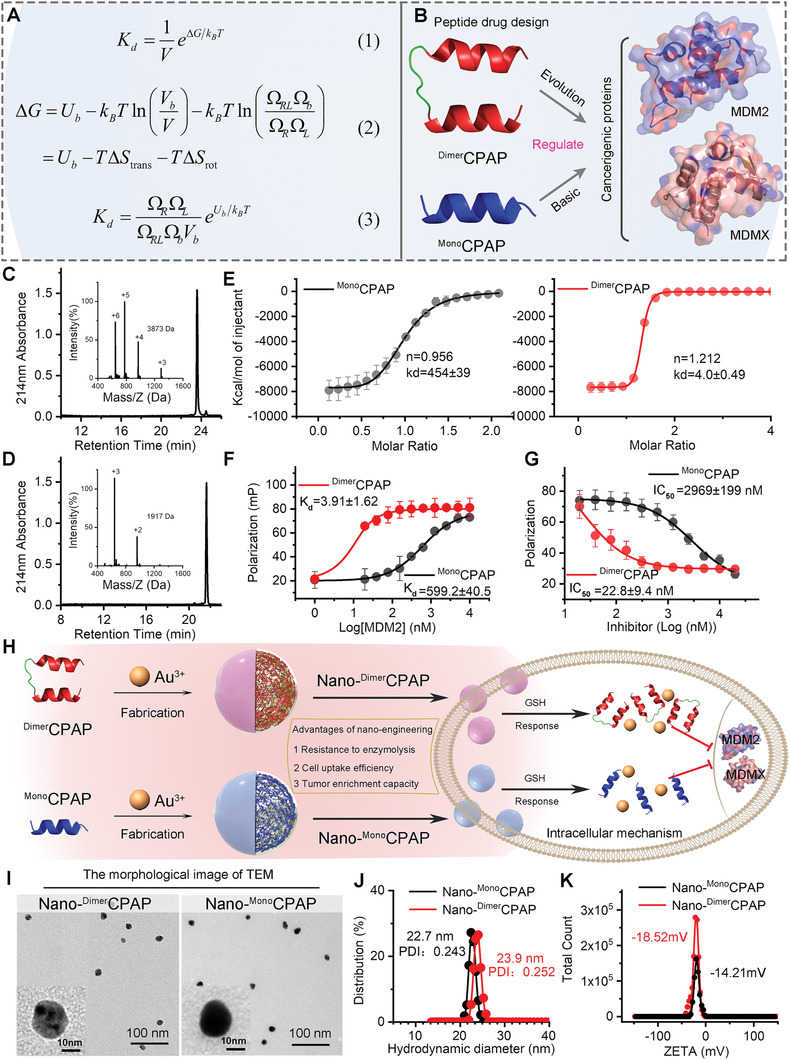
Statistical mechanics theory for binding affinity of dimeric strategy in the intervention of disease PPIs. A) Illustration of the statistical mechanics theory. B) The schematic diagram of function of DimerCPAP and MonoCPAP. C,D) DimerCPAP and MonoCPAP analyzed by HPLC and electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (ESI‐MS), which was performed on a reversed‐phase C18 column (Waters XBridge 3.5 µm, 4.6 × 150 mm) at 40 °C. E) Quantification of the interactions of synMDM2 with varying concentrations of DimerCPAP and MonoCPAP by isothermal titration calorimetry (ITC). Each curve is the mean of 3 independent measurements at 25 °C in 10 × 10−3 m HEPES, 150 × 10−3 m NaCl, pH 7.4. F) Fluorescence polarization (Fp) binding assay of DimerCPAP or MonoCPAP to MDM2 protein. G) Competitive FP‐based binding assay of DimerCPAP or MonoCPAP to MDM2/p53 complex. H) Schematic depiction for nano‐engineering modification of DimerCPAP and MonoCPAP. I) TEM images of Nano‐DimerCPAP and Nano‐MonoCPAP. J) Hydrodynamic diameter and K) ZETA potential of Nano‐DimerCPAP and Nano‐MonoCPAP measured in PBS buffer at pH 7.4.
