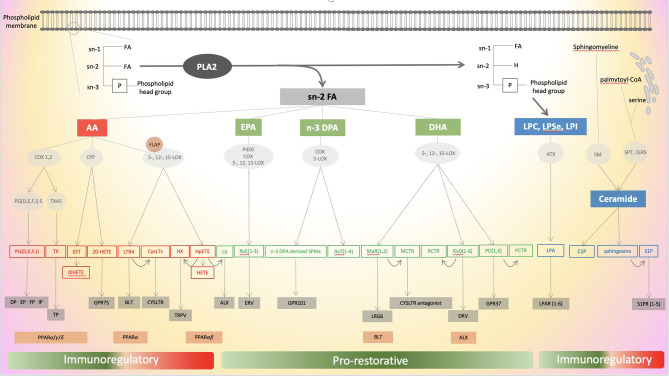
Figure 1.
Schematic illustration of the different pathways of eicosanoids, specialized pro-resolving mediators (SPMs) and lysophospholipids metabolism. Eicosanoid’s mediators are in red, SPMs mediators in green and lysophospholipids mediators in blue. Enzymes are in round grey areas, common receptors in rectangular grey areas and alternative receptors in rectangular orange areas. ATX, autotaxin; BLT, leukotriene receptor, C1P, ceramide-1-phosphate; CERS, ceramide synthases; COX, cyclooxygenase; PLA2, phospholipase A2; CYP, cytochrome P450; CysLTs, cysteinyl leukotrienes; CysLTR, cysteinyl leukotrienes receptors; DHA, docosahexaenoic acid; DP, prostaglandin D receptor; DPA, docosapentaenoic acid; EET, epoxyeicosatetraenoic acid; EP, prostaglandin E receptor; EPA, eicosapentaenoic acid; ERV, E-series resolvin receptor; FA, fatty acid; FLAP, 5-LOX activating protein; FP, prostaglandin F receptor; GPR, G protein-coupled receptor; HETE, hydroxy eicosatetraenoic acid; HpETE, hydroperoxy eicosatetraenoic acid; Hx, hepoxilin; IP, prostacyclin receptor; LGR6, leucine-rich repeat containing G protein-coupled receptor 6; LTB4, leukotriene B4; LOX, lipoxygenase; LPA, lysophosphatidic acid; LPAR, lysophosphatidic acid receptor; LPC, lysophosphatidylcholine; LPSe, lysophosphatidylserine; LPI, lysophosphatidylinositol; LX, lipoxin; MaR, maresin; MCTR1, maresin conjugates in tissue regeneration 1; PCTR, protectin conjugates in tissue regeneration; PD, protectins; PG, prostaglandin; PGS, prostaglandin synthase; PPAR, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor; RvD, D-series resolvin; RvE, E-series resolvin; RvT, thirteen-series resolvin; S1P, Sphingosine-1-phosphate; S1PR, Sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor; SM, sphingomyelinase; SPMs, specialized pro-resolving mediator; SPT, serine -palmitoyl transferase; TRPV, transient receptor potential vanilloide 1; TP, thromboxane receptor; Tx, thromboxane; TXAS, TxA synthase.