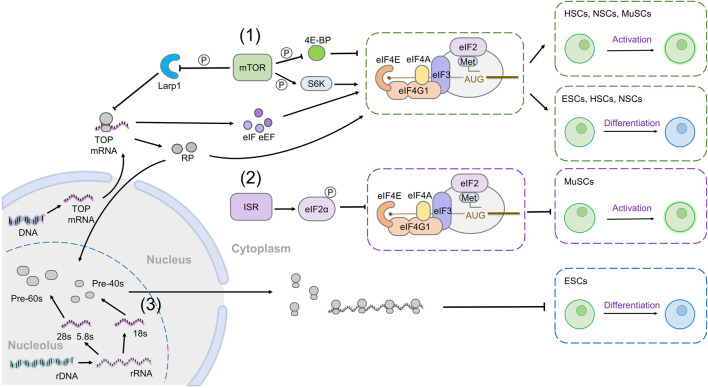
FIGURE 2.
Global mechanisms of translation regulation and their roles in stem cell maintenance. (1) mTOR activity increases global translation through its effectors 4E-BP and S6K and promotes cap-dependent translation. In addition, mTOR increases the translation of TOP mRNAs, which include most components of the translation machinery including translation initiation factors (eIFs), translation elongation factors (eEFs), and ribosomal proteins (RPs). Increased mTOR signaling leads to the activation of HSCs, NSCs, and MuSCs from quiescence and induces differentiation of ESCs, HSCs, and NSCs (green boxes). (2) The integrated stress response (ISR) pathway promotes eIF2ɑ phosphorylation, which reduces eIF2ɑ association with Met-tRNAi Met and impairs global translation. P-eIF2ɑ prevents MuSC activation from quiescence (purple box). (3) Ribosomes are assembled in the nucleolus. Decreasing the rate of ribosome biogenesis results in ESC differentiation (blue box).