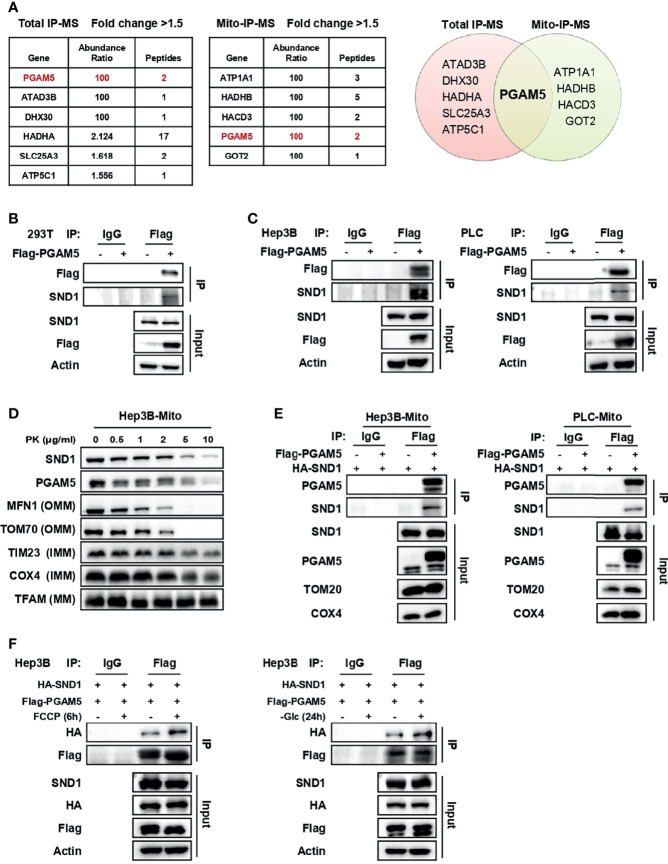
Figure 3.
SND1 binds to PGAM5 in mitochondria. (A) Proteins bound by SND1 with a fold change > 1.5 compared to the EV control group in total IP-MS or mitochondrial IP-MS results (left). Venn diagram showing the overlap of proteins bound by SND1 from total IP-MS and mitochondrial IP-MS results (right). (B) 293T cells were transfected with Flag-EV or Flag-PGAM5 plasmids. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-Flag antibody, followed by immunoblotting analysis with antibodies against Flag and SND1. Actin served as loading control. (C) Hep3B cells (left) or PLC cells (right) stably expressing Flag-PGAM5 were harvested and subjected to Co-IP analysis. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-Flag antibody, followed by immunoblotting analysis with antibodies against Flag and SND1. Actin served as loading control. (D) Protease protection assays performed on purified mitochondria isolated from Hep3B cells. Enriched mitochondria were digested after incubation with proteinase K at the indicated concentrations and the localization of PGAM5 was analyzed by immunoblotting. MFN1/TOM70, TIM23/COX4, and TFAM were used as markers of OMM, IMM, and MM, respectively. (E) Hep3B cells (left) or PLC cells (right) stably expressing HA-SND1 were further infected with viruses expressing Flag-EV or Flag-PGAM5, and then Co-IP assays were performed using an anti-Flag antibody in enriched mitochondrial fractions, followed by immunoblotting analysis with antibodies against PGAM5 and SND1. TOM20 and COX4 served as loading control. (F) Hep3B cells stably expressing HA-SND1 were further infected with viruses expressing Flag-PGAM5, and then treated with FCCP for 6 h (left) or glucose-free medium (right) for 24 h. Cells were harvested and cell lysates were subjected to Co-IP analysis using an anti-Flag antibody, followed by immunoblotting analysis with antibodies against HA, Flag, and SND1. Actin served as loading control.