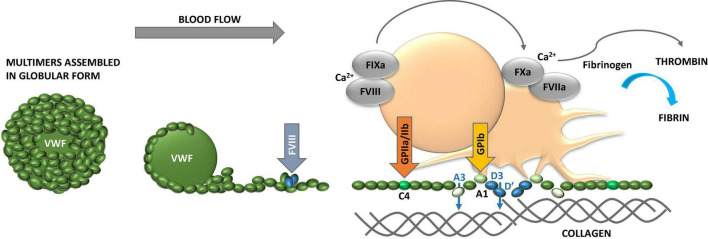
FIGURE 2.
Properties of von Willebrand factor (VWF). VWF obtains globular conformation under static conditions, while it unfolds and elongates under blood flow. The higher the hematocrit, the faster the flow conditions and the smaller the vessel lumen (vasoconstriction), the higher the shear forces and contribution of adhesive platelets. VWF multimer size is controlled by ADAMTS13. While unfolding VWF exposes domains with binding sites for several extracellular proteins, including collagen, and glycosaminoglycans (GAG), and platelet glycoprotein (GP) Ib and GPIIb/IIIa to foster platelet adhesion and activation. VWF carries coagulation factor VIII (FVIII) and liberates it to the tenase complex on platelet surface to support generation of thrombin and formation of fibrin. VWF binds to fibrin as well. The multiple coordinated actions of VWF in platelet recruitment and coagulation pathway are critical in microvascular thrombosis, including thrombo-inflammatory settings.