Figure 1.
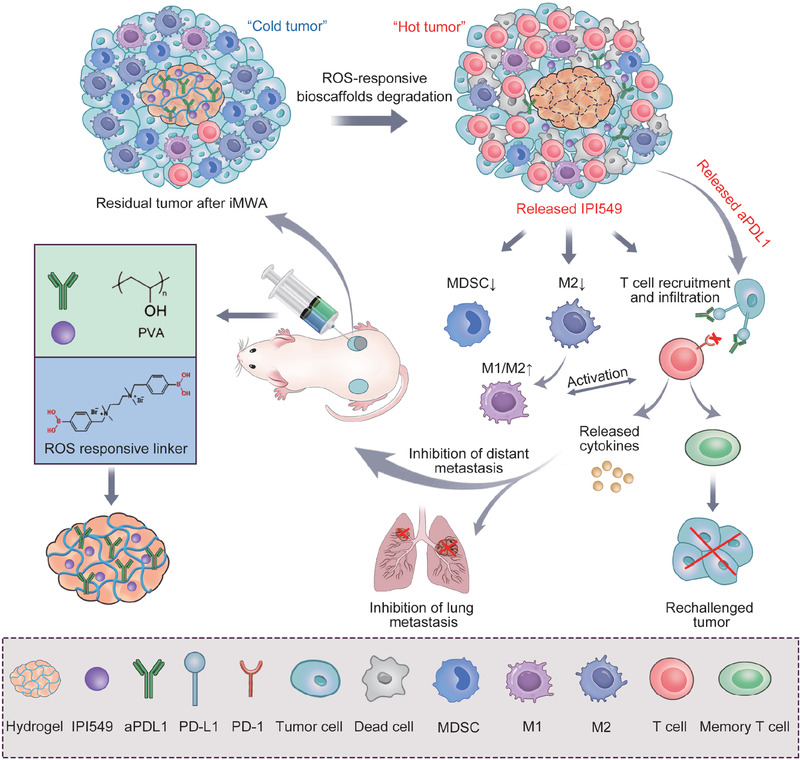
Schematic of engineering ROS‐responsive bioscaffolds disrupting myeloid cell‐driven immunosuppressive niche to enhance PD‐L1 blockade‐based postablative immunotherapy. Inadequate microwave ablation (iMWA) induces immunosuppressive niche predominated by myeloid cells. The in situ gelation involved in this strategy enables local retention and controlled release of therapeutics (aPDL1 and IPI549), in which IPI549 capable of targeting myeloid cells‐induced immunosuppression and subsequently improving PD‐L1 blockade‐mediated antitumor immune response. This biomaterial system (aPDL1&IPI549@Gel) mimics a “hot” tumor‐immunity niche to inhibit tumor progression and metastasis, and protect cured mice against tumor rechallenge. ROS, reactive oxygen species; aPDL1, anti‐programmed death‐ligand 1 blocking antibody; PD‐L1, programmed death‐ligand 1; PD‐1, programmed death‐1; MDSC, myeloid‐derived suppressor cell; M1, M1‐like macrophage; M2, M2‐like macrophage.
