FIGURE 4.
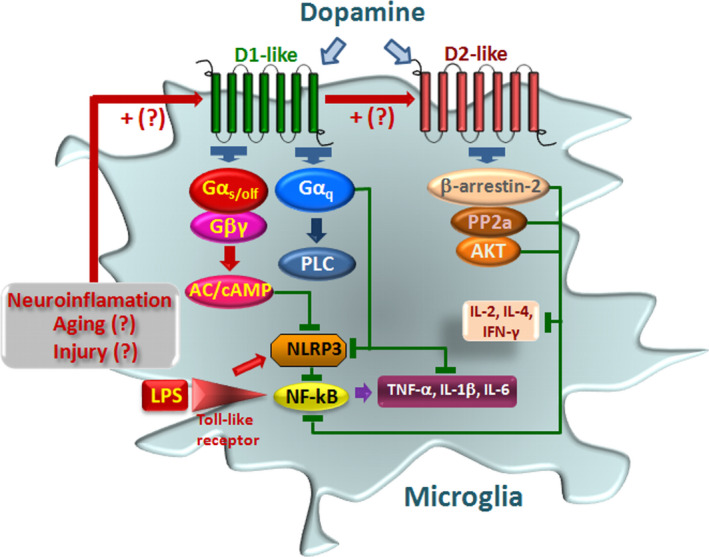
Dopamine signaling pathways modulate inflammasome activation in microglia. Immune activation is schematically represented. LPS via Toll‐like receptors (TLRs) activates Nod‐like receptor protein 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome and nuclear factor kappa‐light‐chain‐enhancer of activated B cell (NF‐ĸB) signaling pathways promoting proinflammatory cytokine (IL‐1β, TNF‐α, IL‐6) release (detailed in Section 1.2). DA and DA agonist activation of D1‐like receptors (D1 and D5) results in a downmodulation of immune response. D1 activation via Gαsolf increases cAMP, which binds directly to NLRP3 triggering its ubiquitination via an autophagy‐mediated degradation. Activated cAMP signaling also inhibits p65/RelA and p50 activation. D5R activation directly recruits a multiprotein complex, impairing activation of NF‐kB. Activation of D2R‐b‐arrestin‐2 complex also results in D2R binding to NLRP3 to repress its activation. D2R signaling can negatively regulate the NF‐kB signaling pathway, thereby inhibiting major proinflammatory cytokine release. The hypothetical role of neuroinflammation, aging, and brain injury, as a counter‐regulatory mechanism, via upregulation of DA receptor expression is illustrated
