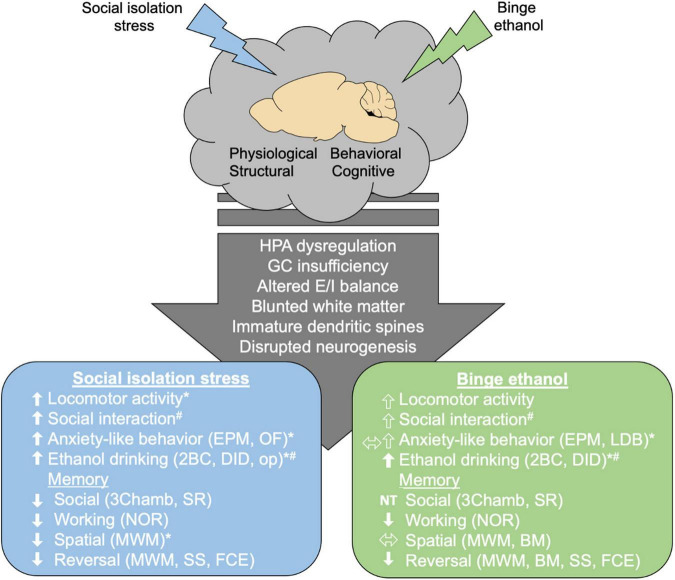
FIGURE 1.
Effects of social isolation stress or binge ethanol in adolescence. The adolescent period is characterized by physiological and structural changes that help mature brain connectivity leading to adult typical behavior and cognition. Postweaning social isolation or binge ethanol in adolescence (∼PND 28–50) alters HPA function, brain connectivity, and generally retains adolescent phenotype (decreased white matter and improper dendritic spine pruning). As reviewed, social isolation stress or binge ethanol increased social interaction, anxiety-like behavior and ethanol drinking. Memory deficits were found following both paradigms. * Indicates conflicting findings in some studies. # Indicates sex differences were reported. Arrow outlines indicate that the effect depends if acute ethanol is used. HPA, hypothalamic pituitary adrenal axis; GC, glucocorticoid; E/I, excitatory/inhibitory; EPM, elevated plus maze; OF, open field; LDB, light dark box; 2BC, 2-bottle choice; DID, drinking in the dark; op, operant responding; 3chamb, 3-chamber social interaction task; SR, social recognition; NOR, novel object recognition; MWM, Morris water maze; BM, Barnes maze; SS, set shifting; FCE, fear conditioned extinction.