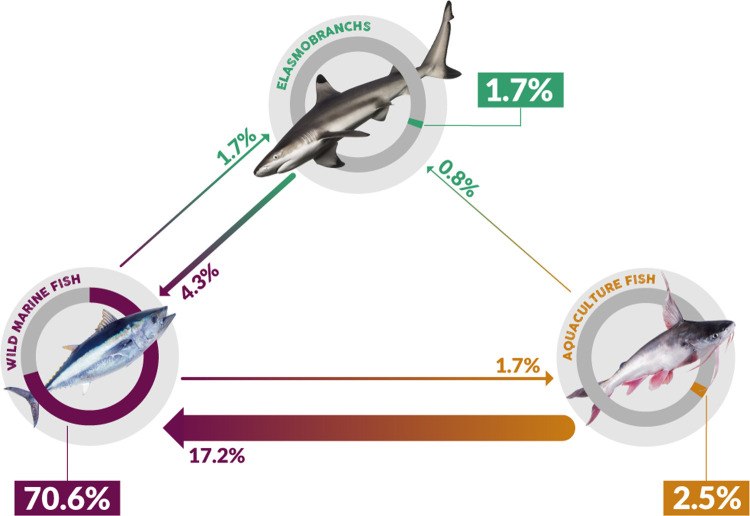
Fig 2.
Patterns of substitution of species within and between three distinct broad groups: a) wild marine bony fishes; b) wild marine elasmobranchs; c) freshwater and anadromous bony fishes from aquaculture. Arrows show each of eight observed types of substitutions, and numbers show the observed frequency (%) of each type. Line widths are proportional to the frequency of a given substitution combination observed. The possible substitution combinations are 1) substitution between two marine bony fishes; 2) substitution of an elasmobranch by a marine bony fish; 3) substitution of a marine bony fish by an elasmobranch; 4) substitution of a marine bony fish by a freshwater bony fish from aquaculture 5) substitution between freshwater bony fishes from aquaculture; 6) substitution of a bony fish from aquaculture by a marine bony fish; 7) substitution between elasmobranchs; 8) substitution of an elasmobranch by a freshwater bony fish from aquaculture. The substitution of a freshwater fish from aquaculture by an elasmobranch was the only possible substitution type not observed.