Fig. 2.
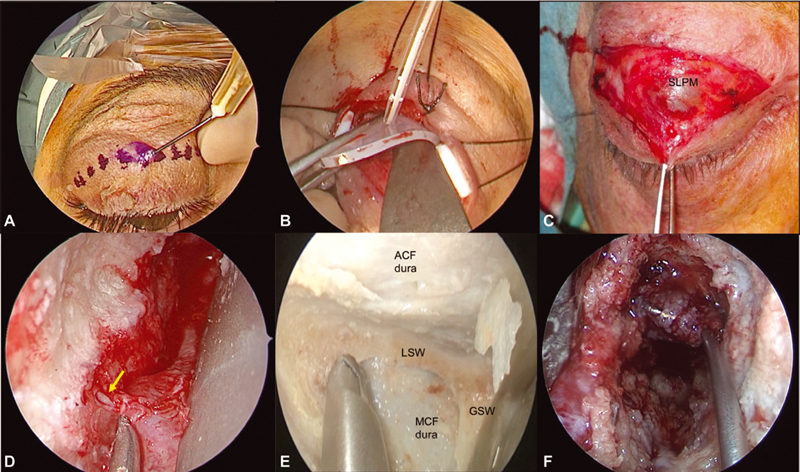
The endoscopic superior eyelid transorbital approach. Skin incision is made on a lid crease superior to the eyelid ( A ), elevating the skin–muscle flap and preserving the upper eyelid retractor system ( B,C ). Stitches and small silastic tubes may help during the first stages of the surgery ( B ). The orbital rim is reached and the subperiosteal dissection begins. Close to superior orbital fissure (SOF), Hyrtl's foramen or meningo-orbital foramen can be found, and the recurrent meningeal artery ( yellow arrow , D ) may be safely coagulated and cut. When reaching SOF and inferior orbital fissure (anatomical dissection image, E ), depending on the surgical target, the drilling of LSW or GSW may open the ACF or MCF (as in F ), respectively. ACF, anterior cranial fossa; GSW, greater sphenoid wing; LSW, lesser sphenoid wing; MCF, middle cranial fossa; SLPM, superior levator palpebrae muscle.
