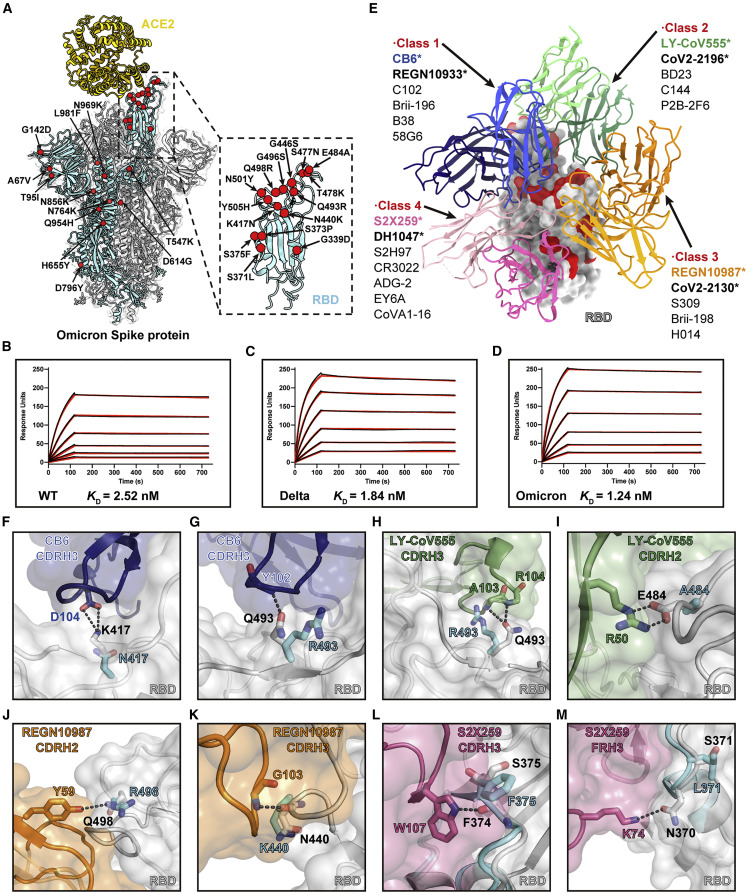
Figure 2.
Analysis of the Omicron spike RBD mutations in ACE binding and antibody evasion
(A) Model of Omicron spike protein with Cα of all mutated residues shown as red spheres.
(B–D) SPR analysis of the WT (B), Delta (C), and Omicron (D) spike protein affinities for human ACE2. The dissociation constant (KD) indicates mean ± SD of three independent replicates. Raw data is colored in black, and the red lines represent the fit to the raw data.
(E) Structural depiction of summarized Abs binding the RBD epitopes. A representative Ab from each class is shown. The Abs reported to be escaped by the Omicron variants are marked with stars.
(F–M) Structural details of the interface between neutralizing antibody Fabs and RBD. The Omicron RBD mutations S371L (M), S375F (L), K417N (F), N440K (K), E484A (I), Q493R (G and H), and Q498R (J) are likely to introduce steric clashes and/or abolish the specific hydrogen bonds.