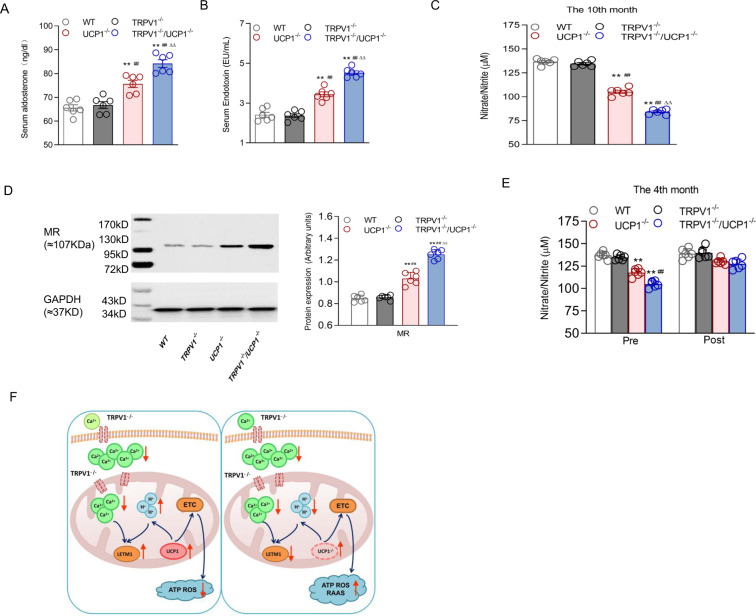
Fig. 7.
Elevated blood pressure induced by TRPV1 knockout synergizing with UCP1 knockout through the activation of the RAA system and ROS production. A–C Serum aldosterone (A), endotoxin (B) and NO (C) were detected in WT, TRPV1−/−, UCP1−/− and TRPV1−/−/UCP1−/− mice. D Immunoblots of mineralocorticoid receptors (MRs) in the white adipose tissue of WT, TRPV1−/−, UCP1−/− and TRPV1−/−/UCP1−/− mice. E The pre- and post-tempol (3 mmol/L in drinking water)-treated serum NO of WT, TRPV1−/− and UCP1−/− mice. F The working model for the deficiency of TRPV1 (left) and TRPV1&UCP1 double knockout (right) in brown adipose tissue causes obesity and the associated hypertension. TRPV1 knockout aggravates the dysfunction of [Ca2+]mito uptake caused by UCP1 knockout, increases the production of ATP and ROS, activates the RAA system, and leads to higher body weight and blood pressure. Values are presented as the means ± SEM for six experiments. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 vs. WT mice; #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01 vs. TRPV1−/− mice; ∆P < 0.05, ∆∆P < 0.01 vs. UCP1−/− mice