Fig. 4.
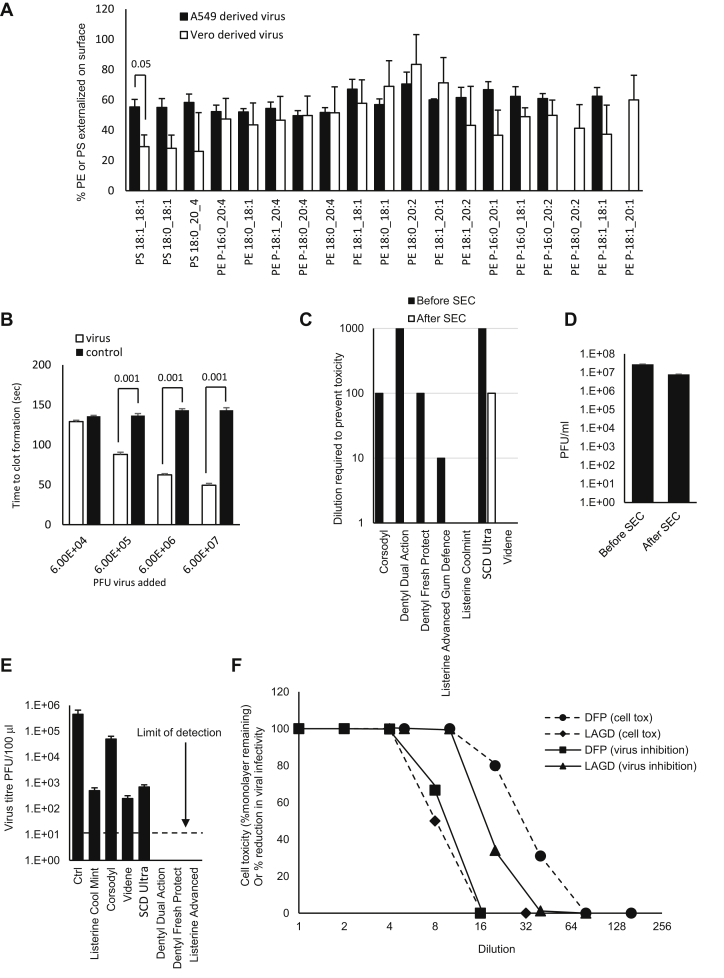
SARS-CoV2 membranes externalize large proportions of PE and PS on the surface of the particles, virus can enhance plasma coagulation, and virions are sensitive to inactivation by surfactants in widely available oral rinses beyond the level required for EN14476 standard. A: High external exposure of aPL on the surface of SARS-CoV2. External PS and PE were determined as described in the Materials and methods section for three preparations of SARS-CoV2 (n = 3, mean ± SEM) using virus from A549 or Vero cells as indicated, unpaired Student's t-test. B: Virions enhance plasma coagulation. Virus was added to normal human plasma as outlined in the Materials and methods section, and time to gel/clot formation was measured. PBS was added to control samples. n = 3, ± SEM, one-way ANOVA with Tukey post hoc test. C: Size-exclusion chromatography (SEC) can remove mouthwash to prevent any direct impact on cell viability during infectivity testing. Mouthwashes were mixed with DMEM and synthetic salivary secretions, then 100 μl of the mixture was purified through a S-400 HR spin column, diluted by serial 10-fold dilution in DMEM/10, and inoculated onto VeroE6/ACE2/TMPRSS2. After 72 h, overlays were removed, and monolayers were fixed and stained with crystal violet, then toxicity was scored based on visual inspection of monolayer integrity (mean, n = 2, representative of three independent experiments). D: Removal of mouthwash using SEC has little impact on viral infectivity. Viruses (100 μl) were purified through an S-400 HR spin column, and live virus was measured by plaque assay on VeroE6/ACE2/TMPRSS2 (n = 3–4, mean ± SEM). E: Several mouthwashes can significantly reduce infectivity, whereas some totally eradicate the virus, achieving the EN14476 standard. Virus was mixed with synthetic salivary secretions and mouthwash and then purified by SEC after 30 s, before being titrated by plaque assay on VeroE6/ACE2/TMPRSS2 as described in the Materials and methods section (n = 2, mean ± SD, representative of three independent experiments). F: Comparing selectivity for virus inactivation versus host cell toxicity reveals differential effects. For cell toxicity, serial 2-fold dilutions of dental fresh protect (DFP) or Listerine Advanced Gum Defense (LAGD) were made, then added to VeroE6/ACE2/TMPRSS2 monolayers for 30 s, washed off, and replaced with media. Three days later, monolayers were stained with crystal violet and scored for toxicity. For virus infectivity, serial 2-fold dilutions of mouthwashes were made and then incubated with SARS-CoV2 and a soil load for 30 s. After purification by SEC, samples were titrated by plaque assay on VeroE6/ACE2/TMPRSS2. Inhibition was calculated relative to virus incubated with media alone (n = 1 [virus toxicity] or 2 [cell toxicity, mean], representative of three independent experiments).